| Telescopes |
|---|

|
|
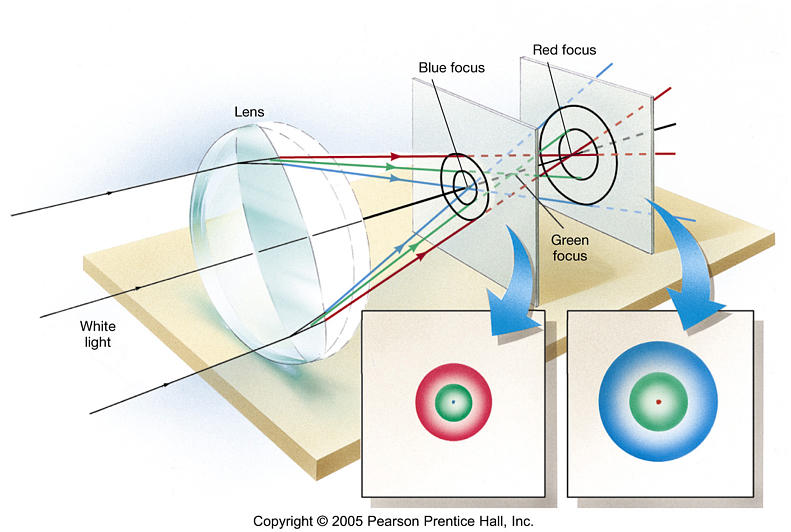
Chromatic aberration |

|
1) avoids chromatic aberration
2) easier to mount (lighter and can support from back)
3) Limited by turbulence and disturbances in air that
twinkle stars
10 meter - Keck at Mauna Kea, Hawaii
Best observing conditions in the world:
Mauna Kea Volcano, Hawaii - 14,000 feet
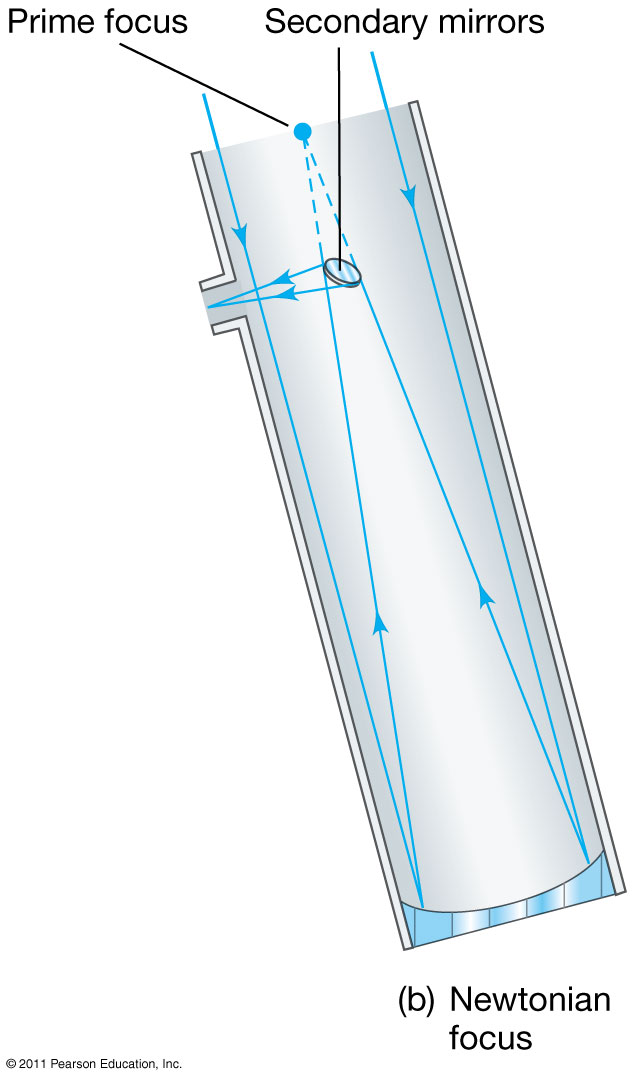
| 
| ||
|
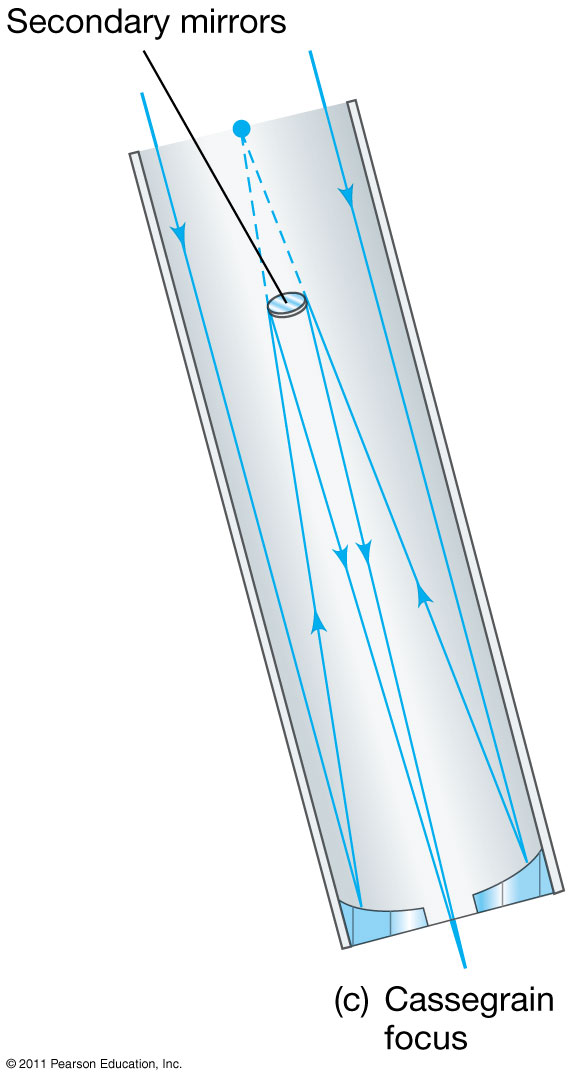
|
angular resolution (arc sec) = 0.25 wavelength(microns) / diameter(meters) |
|---|
Examples:
200 inch Palomar Observatory
has twice the resolving power
has four times the light gathering power
of the 100 inch Mt. Wilson Observatory
Invented during the 19th century and served astronomers well
Advantage: Long-term storage of information
However "Old Fashioned"
e.g. only records 5% of light
Silicon device:
Send data directly from CCD to Computer
"Electronic" image
Uses (records) as much as 90% of light
Radio Telescopes: Made from dishes
which focus the radio signals on a receiver.
The RESOLVING POWER for radio signals is inherently worse
than for visible light due to the much LONGER wavelength.
angular resolution (arc sec) = 0.25 wavelength(microns) / diameter(meters) Examples |
|---|