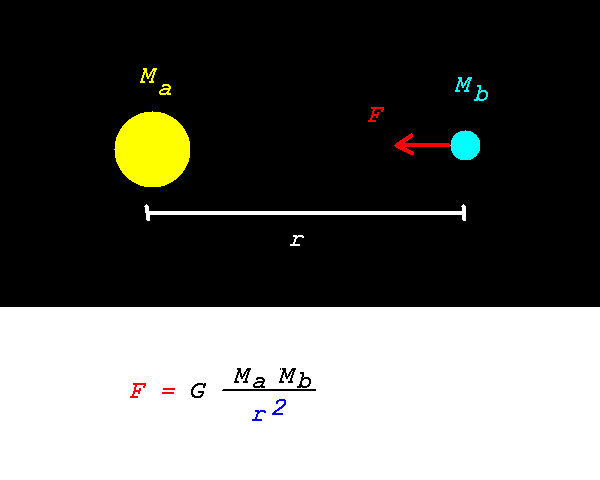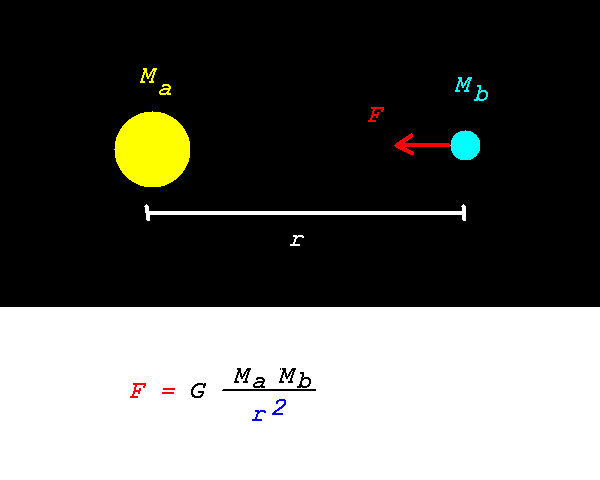Newton's Law of Gravity
Each object in the universe attracts each other body.
If object A has mass Ma and object B has mass Mb,
then the force F on object A
is directed toward object B
and has magnitude
F = G Ma Mb / r2
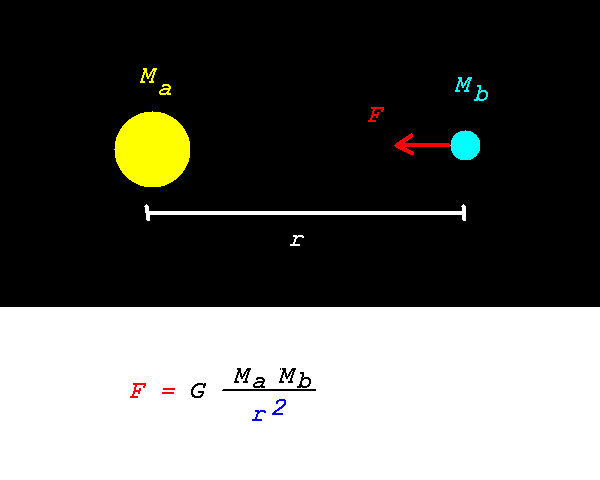
So, considering the force between an Sun and the Earth
- The force exerted on the Earth by the Sun is equal and opposite
to the force exerted on the Sun by the Earth.
- If the mass of the Earth were doubled, the force on the Earth
would double.
- If the mass of the Sun were doubled, the force on the Earth
would double.
- If the Earth were twice as far away from the Sun,
the force on the Earth would be a factor four smaller.
Notes on the meaning of r:
- If the two objects are very small compared to the distance between
them, then the force is given by Newton's formula with r
being the distance between the objects.

- If one of the objects is very small and the other is spherically
symmetric, then the same formula holds with r
being the distance from the small object to the center of the big
object.
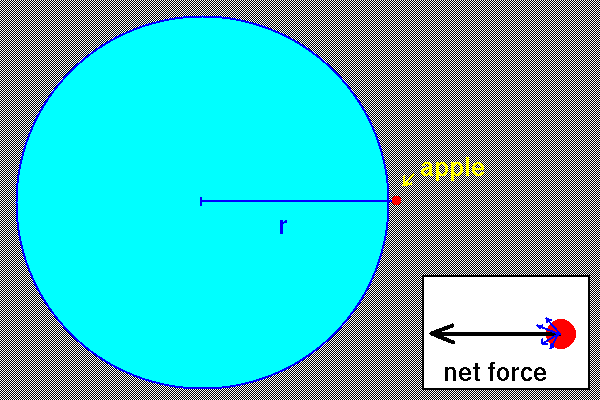
- Point two is a consequence of point one. Newton proved it
by adding up the forces.
But how could you measure G ?
ASTR 121 Home
Davison E. Soper, Institute of Theoretical Science,
University of Oregon, Eugene OR 97403 USA
soper@bovine.uoregon.edu