Continuous Spectrum and Temperature
Blackbody Radiation
The continous part (the smooth part) of the spectrum of most stars
resembles the spectrum of idealized radiators known as
blackbodies. Blackbodies are materials
which are absolutely perfect absorbers of energy, they absorb all
wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation which strikes their
surfaces. They are perfectly black.
Material such as
soot are
very black and nearly blackbody in character. However, interestingly,
it may be the Universe itself which forms the most perfect blackbody we have
yet detected (The Cosmic Microwave Background radiation has a nearly
perfect blackbody spectrum).
These idealized objects are very simple
in nature. Their properties do not depend upon their
chemical composition, their shapes, their sizes, their ages, their
luminosities,
their masses, their ..., the only thing their properties depend upon is their
temperature!
The emission spectrum of a blackobdy is easily calculated because of its
simple nature. Their spectra
are referred to as
blackbody
spectra or Planck curves. They are exceedingly simple in
character; their emission is characterized by only their
temperature T .*Again, n`othing else matters, their
shapes, sizes, what they are made of, and so has no bearing on how
they radiate! The extremley
happy circumstance is that stars radiate
in a manner which can roughly be described as blackbody. We
use this fact, below and later.
(1) A simple measure of the temperature of a star
may be based on its color because we know from studies on blackbodies
in Terrestrial laboratories and theoretical musings,
that the spectra of blackbody radiators of different temperatures
look like;

The higher the temperaure of a blackbody, the more it radiates at all
wavelengths, but relatively speaking, the bluer it will appear
(the shorter the wavelngth) at which the peak of its intensity falls. Compare
the 12,000 K spectrum to the 3,000 K spectrum above.
The color of a star (blackbody)
is then determined by its temperature. Cooler
stars produce relatively larger
amounts of red light compared to blue light than do hotter stars.
(2) In addition to simply using the color of a star to infer its temperature,
we can also use the information contained in
Wien's law,
W(max) = 0.3 cm - Kelvin / T(K),
to infer
precise temperatures for stars. In the above T(K)
is the temperature as measured in
Kelvin. The wavelength inferred from the Wien Law is in centimeters if the above
expression is used. Wien's Law says that the wavelength at
which a blackody radiator is the brightest is determined by the inverse of
its temperature.
Below, we show the Solar spectrum.
The Sun is indeed fairly well-represented by a
blackbody spectrum:
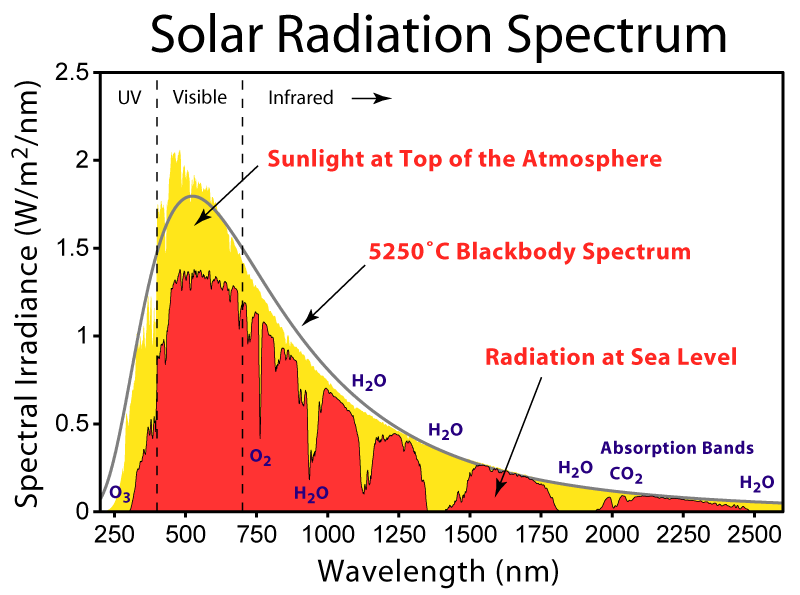 In the above, the example blackbody shown has temperature T = 5,250 C + 273 C =
5,523 Kelvin.
In the above, the example blackbody shown has temperature T = 5,250 C + 273 C =
5,523 Kelvin.
Let's estimate the temperature of the Sun using
Wien's Law,
W = 0.3 cm-K / T(K). Looking at the spectrum we see that the
Sun is the brightest at a wavelength
of 5.4x10-5 cm (see the above plot but note
that the wavelengths are measured in nm = nano-meters = 10-9 meters
= 10-7 cm). Then the temperature of the Sun is given by
T(K) = 0.3 cm-K / W = 0.3 cm-K /
5.2x10-5 cm =
5.8x103 K
The surface temperature of a star may be determined by locating the wavelength
at which it radiates the most strongly
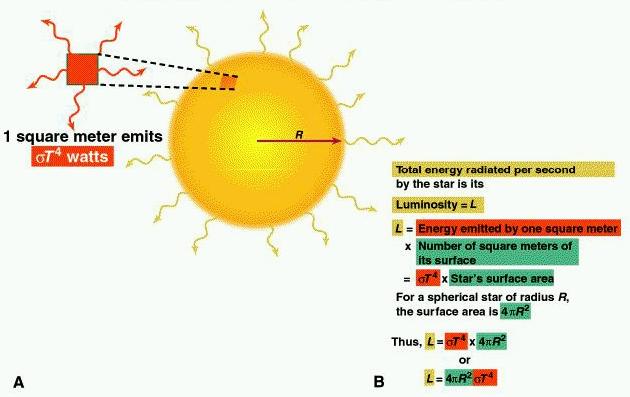
By itself, the Stefan-Boltzmann law is interesting but when used in
conjunction with other known quantities, it can be used to infer properties
of a star. For example, if a star radiates like a blackbody, then
the luminosity of the star can be written as
L = (Surface Area of the Star) x (power per unit area produced by the star)
= 4πR2σT4
So, if we know certain information (obtained through independent means)
about a star, we can infer other properties.
For example,
- If we know the luminosity and temperature, we can infer the radius of
the star;
- If we know the luminosity and radius of a star,
we can infer its temperature;
- If we know the radius and temperature of a star, we can infer its
luminosity
The point is, we cannot use the Stefan-Boltzmann law to infer properities
of a star based on an observation,
unless we have already certain (independently obtained)
information in hand. It is not a
way to directly measure properties of a star.