Inserting Drawings as External References
You can attach xrefs to create
subassemblies that make up a drawing. You can overlay xrefs to check
how your drawing relates to other drawings.
Attaching or overlaying an xref is
similar to inserting an entire drawing as a block. The contents of
the specified drawing, except for overlaid xrefs, are copied into a
new block definition. Instances of the xref in the drawing are block
references.
When you open or plot a drawing
containing xrefs, AutoCAD LT automatically reloads the latest
version of each xref.
To insert a XREF go to
Insert>External Reference or type XREF at the command prompt.
External Reference Dialog Box
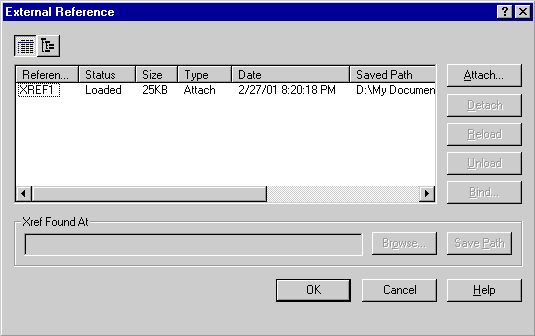
Attaches, overlays, lists, binds,
detaches, reloads, unloads, renames, and modifies paths to external
references (xrefs) in the current (or host) drawing.
Dialog Box Options
- List of external references (List
View and Tree View)
- Attach (displays the Attach Xref
dialog box)
- Detach
- Reload
- Unload
- Bind (displays the Bind Xrefs
dialog box)
- Browse
- Save Path
List of External References
List View
Displays a flat listing of the
attached xrefs and their associated data. You can sort the list of
references by name, status, type, file date, file size, or the saved
path and file name.
Selecting any field highlights the
xref name and selects the xref.
- Reference Name. Lists the
names of the xrefs as stored in the block definition symbol
table.
- Status. Shows whether the
xref is loaded, unloaded, unreferenced, not found, unresolved,
orphaned, or marked for unloading or reloading.
- Size. Shows the file size
of the corresponding reference drawing. The size is not
displayed if the xref is unloaded, not found, or unresolved.
- Type. Indicates whether the
xref is an attachment or an overlay.
- Date. Displays the last
date the associated drawing was modified. This date is not
displayed if the xref is unloaded, not found, or unresolved.
- Saved Path. Shows the saved
path of the associated xref (this is not necessarily where the
xref is found).
Tree View: Displays
a hierarchical representation of the xrefs, displaying the
relationships between xref definitions. Tree view shows the level of
nesting relationship of the attached xrefs, whether they are
attached or overlaid, and whether they are loaded, unloaded, marked
for reload or unload, or not found, unresolved, or unreferenced.
You can also use the F3 and F4 keys
to toggle between list view and tree view.
Attach: Displays the Attach
Xref dialog box or the Select File to Attach dialog box.
Detach: Detaches
one or more xrefs from your drawing, erasing all instances of a
specified xref and marking the xref definition for deletion from the
symbol table. Only the xrefs attached or overlaid directly to the
current drawing can be detached; nested xrefs cannot be detached.
AutoCAD LT cannot detach an xref referenced by another xref or
block.
Reload: Marks
one or more xrefs for reloading. This option rereads and displays
the most recently saved version of the drawing.
Unload:
Unloads one or more xrefs. Unloaded
xrefs can be easily reloaded. Unlike detach, unloading does not
remove the xref permanently. It merely suppresses the display and
regeneration of the xref definition, to help current session editing
and improvement of performance.
Bind: Displays
the Bind Xrefs dialog box.
Browse:
Displays the Select New Path dialog box, in which you can select a
different path or file name.
Save
Path: Saves the path, as it
appears in the Xref Found At field, to the currently selected xref.
|
![]()
