1) The concept of opportunity cost (a) is relevant only for a capitalist economy like the United States. (b) suggests all our wants can be achieved. (c) would be irrelevant if we eliminated poverty. (d) suggests a major increase in public health-care spending means an expansion in other area will be harder to achieve. 2) You decided that for Halloween you wanted to dress up as Batman. You estimated that it would cost $25 to purchase all the pieces of the costume. After spending $20 on the costume you realize that the additional pieces you need will cost you $15 more. The marginal cost of completing the costume is (a) $5. (b) $10. (c) $15. (d) $20. 3) Which of the following is NOT an opportunity cost of attending college? (a) The tuition you pay. (b) The income you could have earned if you didn't attend college. (c) The alternative uses of the time you spend studying. (d) The cost of the food that you consume while you are attending college. 4) The common expression which describes the efficient markets hypothesis is (a) no use crying over spilt milk. (b) there's no such thing as a free lunch. (c) sunk costs are sunk. (d) correlation does not imply causation. 5) If the opportunity costs of producing a good increase as more of that good is produced, the economy's production possibility frontier will be (a) negatively sloped and "bowed inward" toward the origin. (b) negatively sloped and "bowed outward" from the origin. (c) a negatively sloped straight line. (d) a positively sloped straight line. 6) For an economy to produce at a point beyond its current ppf, the economy must (a) waste less. (b) be more efficient. (c) reduce inputs. (d) increase inputs.

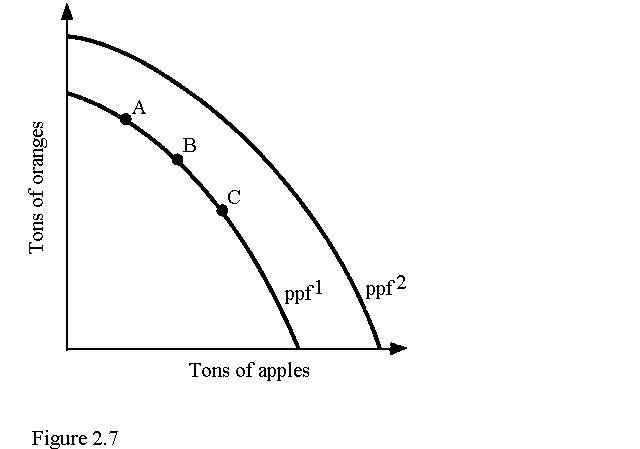
7) Refer to Figure 2.7. An improvement in technology may be represented by a (a) shift from ppf2 to ppf1. (b) shift from ppf1 to ppf2. (c) movement from B to A. (d) movement from C to B along ppf1. 8) Refer to Figure 2.7. The economy may prefer point A to point B because (a) Point A represents a more efficient point on the ppf. (b) Consumers prefer a greater ratio of apple production to orange production. (c) Consumers prefer a greater ratio of orange production to apple production. (d) There is less unemployment at point A than at point B or C. 9) An economy in which a central authority draws up a plan that establishes what will be produced and when, sets production goals, and makes rules for distribution is (a) a socialist economy. (b) a laissez-faire economy. (c) a public goods economy. (d) a command economy. 10) If the unemployment rate decreases from 10 percent to 8 percent, the economy will (a) move closer to the ppf. (b) move away from the ppf toward the origin. (c) remain on the ppf. (d) remain on the origin.