Week 5 Practice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
1) The period of time during which all inputs can be varied is known as
the
a) market period.
b) short run.
c) interim period.
d) long run.
2) Average product
a) increases when marginal product is greater than average product.
b) is defined as total product devided by the quantity of variable input
employed.
c) reaches a maximum when marginal product and average product are equal.
d) all of the above.
3) The law of diminishing marginal return implies that
a) short-run marginal costs will eventually become negative for increases
in production.
b) marginal product must be negative for any input of labor.
c) short-run marginal costs will eventually increase for increases in
production.
d) none of the above.
4) The marginal cost curve:
a) first rises, then declines.
b) intersects the average variable cost and average cost curves from below
at their minimum points.
c) increases when the average cost curve lies above the average variable
cost curve.
d) falls when the point of diminishing marginal returns is reached.
5) If the market wage is $10 and the change in output per hour of labor
employed is 5 units, what is the marginal cost of producting the next unit
of output?
a) $50
b) $15
c) $ 2
d) $0.50
6) When price is less than marginal cost, a profit-maximizing producer in
perfect competition will
a) decrease production
b) increase production
c) raise the price charged by the firm and decrease output.
d) leave the level of output unchanged.
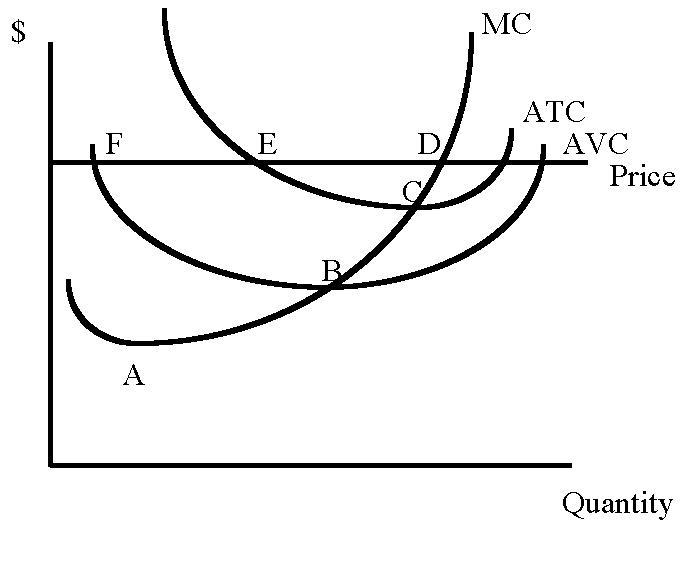
Questions 7-13 refer to the figure above which represents a model of a
perfectly competitive firm.
7) Which point represents the point of diminishing marginal returns?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
8) Which point represents the price and output combination where the firm
would make normal profit, but not economic profit?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
9) Given the price line, which point represents the output level the firm
would choose to maximize profits?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
10) Which point represents the shut-down point for the firm in the short
run?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
11) As diagrammed, the firm is making
a) normal profit, but not economic profit.
b) economic profit, but not normal profit.
c) both normal and economic profit.
d) neither normal nor economic profit.
12) The vertical distance between the ATC and AVC curve represents
a) marginal cost (MC)
b) average fixed cost (AFC)
c) total fixed cost (TFC)
d) total cost (TC) - total variable cost (TVC)
13) Which point represents the level of quantity that minimizes MC?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
14) Which point represents the minimum average variable cost (AVC)?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
15) Which point represents the minimum average total cost (ATC)?
a) point A.
b) point B.
c) point C.
d) point D.
e) point E.
f) point F.
Short Answer
Questions
1) Complete the following table:
Quantity TVC TFC TC AVC AFC ATC MC PRICE
0 0 50 80
1 50 80
2 90 80
3 110 80
4 150 80
5 210 80
6 290 80
7 410 80
After completing the table, you may want to graph AVC, ATC and MC against
Q.
After which quantity level does diminishing marginal returns begin?
Which level of production (quantity) maximizes profit for a
perfectly-competitive firm?
What are profits at the profit-maximizing solution?
2) Think about what would happen if the law of diminshing marginal returns
became the law of increasing marginal returns. What would the marginal
product (MP) graph look like? What would marginal cost (MC), average
variable cost (AVC) and average total cost (ATC) graphs look like? Where
would a profit-maximizing perfectly-competitive firm set quantity? Would
the average fixed cost (AFC) curve change? Does this new law of
increasing marginal returns make sense?
3) What would happen to the cost curves if the firm had no fixed costs?
