
12-October-1999
This exam consists of 15 multiple choice questions (worth 2 points each). Please put your name on the Scantron form and indicate your answers to the questions on it. Important formulae and conversion factors can be found on the last page.
Questions 1-3 refer to the figure above. A monkey-child is playing on a frictionless slide. Any air resistance can be ignored. The positive direction is up the slide, or to the left for the horizontal portion.
_B_1. The child starts sliding at A. Between points A and C, the net (total) force on the child is:
A.?Zero
B.?Constant and non-zero.
C.?Increasing at a steady (constant) rate.
D.?Decreasing at a steady (constant) rate.
E.?None of the above.
_C_2. Between points A and C, the speed of the child is:
A.?Zero
B.?Constant and non-zero.
C.?Increasing at a steady (constant) rate.
D.?Decreasing at a steady (constant) rate.
E.?None of the above.
_B_3. Between points A and C, the acceleration of the child is
A.?Zero
B.?Constant and non-zero.
C.?Increasing at a steady (constant) rate.
D.?Decreasing at a steady (constant) rate.
E.?None of the above.

E is the correct answer.

C is the correct answer.
_E_6)?Three objects, each with the same size but with different masses are dropped from the same height at the same time. Neglect air resistance. Which of the following statements correctly describes and explains how they fall?
A)?They all three hit the ground at the same time. This is because they all three had the same constant velocity while they fell. The force of gravity on each object, however, is different according to their respective masses.
B)?They all three hit the ground at the same time. They all three underwent the same acceleration in falling. The force of gravity on each was the same for each.
C)?The heaviest object hit first, followed by the second heaviest, etc. This is because the force gravity exerts on each object is the same.
D)?The heaviest object hit first, followed by the second heaviest, etc. This is because the acceleration due to gravity is the same for each object.
E)?They all three hit the ground at the same time. This is because all three underwent the same, constant acceleration in falling. The force of gravity on each object was different, according to their respective masses.
_D_7)?Flight 727 takes off from Eugene Airport, flying to Denver. After takeoff it ascends to 32,000 feet altitude, levels off and, finally, descends to land at Denver International Airport. Which of the following statements correctly describes the work and energy status of the plane during the 3 phases (ascent, level flight, descent) of the flight?
A)?During ascent the Earth’s gravity is doing positive work on the plane. The plane is increasing its gravitational potential energy (GPE) during ascent.
B)?During level flight, where the plane is maintaining a constant altitude above the Earth, gravity and the plane do no effective work on one another. The gravitational potential energy of the plane decreases during this time.
C)?During descent into Denver the Earth’s gravity is doing work on the plane. The plane’s GPE remains constant.
D)?During ascent the plane is doing positive work against the Earth’s gravity. The plane is increasing its GPE.
E)?None of the above are correct.
_B_8)?Flight 727 is on its final descent from 32,000 feet to land in Denver. Which of the following statement correctly describes energy conversion for the plane and the pilot's actions?
A)?During descent the Earth’s gravity is doing positive work on the plane. The plane is increasing its gravitational potential energy (GPE) and slowing down. The pilot must gun the engines to maintain air speed.
B)?During descent the Earth’s gravity is doing positive work on the plane. The plane is decreasing its gravitational potential energy (GPE) but increasing its kinetic energy (KE). The pilot must brake using the wing flaps to maintain air speed.
C)?During descent the Earth’s gravity is doing positive work on the plane. The plane is decreasing its gravitational potential energy (GPE) and its kinetic energy (KE). The pilot must gun the engines to maintain air speed.
D)?During descent the Earth’s gravity is doing positive work on the plane. The plane is decreasing its gravitational potential energy (GPE) but increasing its kinetic energy (KE). The pilot must gun the engines to maintain air speed.
E)?None of the above are correct.
_E_9)?The McSpiff family and the McSplurges are driving two identical cars across a flat, dusty town (no hills to climb). However, the McSplurges, as a family, weigh twice as much as the McSpiffs. McSplurges are following the McSpiffs and match their speed as they stop for traffic lights and accelerate up to the speed limit afterwards. Which of the following statements correctly describes this situation?
A)?The McSpiffs and the McSplurges use the same amount of gasoline. Both cars have the same rolling resistance and aerodynamic drag.
B)?The McSpiffs use more gasoline in traveling across town. Their car has to overcome greater rolling resistance.
C)?The McSplurges use more gasoline in traveling across town. The only difference is that the McSplurge’s car has greater rolling resistance.
D)?The McSplurges use more gasoline in traveling across town. The difference is that the McSplurge’s car has greater rolling resistance and aerodynamic drag.
E)?The McSplurges use more gasoline in traveling across town. Their car needs more energy to accelerate from stop lights.
_D_10)?The McSplurges have bought a new "sport ute" ("sport utility vehicle")! It sits 1/2 meter higher off the ground than their old car, which was identical to the McSpiff's car. The two families drive their respective vehicles at 100 km/hr (~65 miles/hr) on the fairly flat road to Portland together. Which of following is the principle reason the McSplurges get poorer gas mileage and pollute the environment with more CO2 during the trip?
A)?The McSplurges weigh more and require more energy to accelerate.
B)?The rolling resistance of the McSplurge's vehicle is greater.
C)?The McSplurges use more energy going up hills.
D)?The McSplurge's vehicle has greater air resistance than the McSpiff's.
E)?The McSplurges and their vehicle weigh more and require more energy to accelerate.
_B_11)?Regarding kinetic energy, which of the following statement(s) is true?
A)?An object’s kinetic energy is proportional to its mass and to its velocity.
B)?An object has energy in motion (kinetic energy) because it can run into another object and do work on that object by changing the latter's motion.
C)?An object’s kinetic energy is inversely proportional to its mass and proportional to its velocity squared.
D)?An object’s kinetic energy is always positive because its mass must be positive and it can’t have a negative velocity.
E)?Both B) and D) are correct.
_C_12)?The rate at which water flows into a hydropower facility primarily controls:
A)?The total energy the facility can produce.
B)?The size of the dam needed to impound water.
C)?The power rating of the facility.
D)?The acceleration the water undergoes in falling to the turbines.
E)?The force on the water in the pipes leading to the turbine.
_E_13)?During the lab session you timed yourself running up a flight of stairs to determine your "personal power rating." You did this by calculating the gravitational potential energy (GPE) you gained in running up the stairs and dividing it by the time it took. Three months, four milkshakes a day and an extra 20 lbs later, you undertake a similar experiment. To your surprise, you find that your personal power rating is unchanged. Which of the following correctly explains this result.
A)?The GPE you gained is the same and the time required to run up the stairs was the same.
B)?The GPE you gained is more, but the time required to run up the stairs is less.
C)?The GPE you gained is less, but the time required to run up the stairs is also less.
D)?The GPE you gained is more, but the time required to run up the stairs is the same.
E)?The GPE you gained is more and the time required to run up the stairs is more.
_C_14)?Professor Dufus has designed a simple experiment to test the energy efficiency of his new moped. On a windless day, he takes the moped to the Great Salt Flats and measures exactly one liter of gas into its tank. He then rides the moped at a constant speed in a straight line until it runs out of gas. By carefully measuring the distance he traveled, he determines the fuel economy (km per liter) of the moped. Later, Prof. Dufus loses his results! To recover, he quickly undertakes the same experiment, only on a curved track. Dufus should not believe that his second experiment replicates his first because:
A)?Although the velocity of the moped is the same both times, the speed is different.
B)?The velocity is different between experiments, while the net force is the same.
C)?The velocity is different between experiments, so the net force on the moped differs.
D)?The speed is the same for both experiments, while the force of gravity is different.
E)?The net force on the moped differs between experiments because the speed is different.
___15)?A ball with mass, m, is tossed upwards towards a motion detector. The ball doesn't reach the motion detector, and finally falls to the ground. Which of the following pairs of velocity/acceleration plots is consistent with the entire motion of the ball after release?
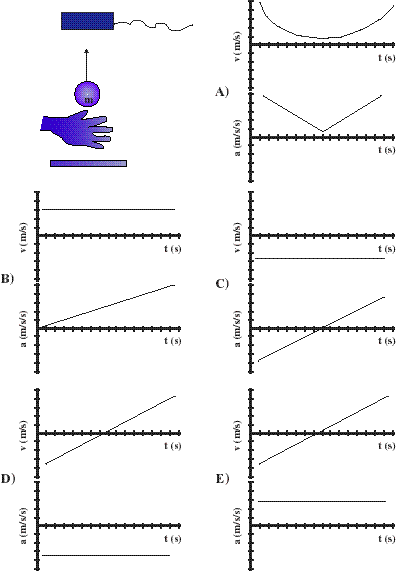
E is the correct answer.