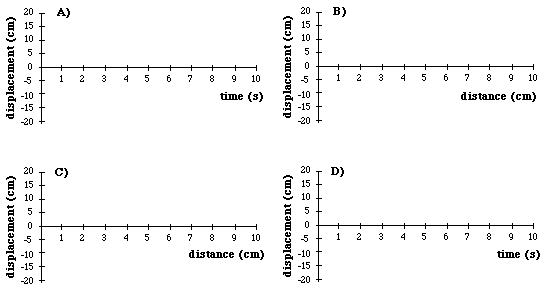Midterm Quiz 2: Physics of Energy & Environment-- PHYS 161
28-October-1999
This exam consists of 15 multiple choice questions (worth 2 points each). Please put your name on the Scantron form and indicate your answers to the questions on it. Important formulae and conversion factors can be found on the last page.
___1) You have developed SUPER powers and can see minute objects, even electrons and protons! To satisfy your curiosity about charge, you take a rubber rod and rub it on cat’s fur. After doing so, you "see" an excess of electrons built up on the rod. Then you hold the rod next to an uncharged pith ball, a small styrofoam ball covered with electrically conducting metal foil. What do you see with your SUPER powers?
A) When the rod is brought near the pith ball, electrons on the latter are pulled to the near side of the ball. An excess of electrons develops on the near side of the pith ball. Because the like-charged near side is closer than the oppositely-charged far side of the pith ball, it is attracted to the rod.
B) When the rod is brought near the pith ball, electrons on the latter are pulled to the near side of the ball. A shortage of electrons develops on the near side of the pith ball. Because the oppositely-charged near side is closer than the like-charged far side of the pith ball, it is attracted to the rod.
C) When the rod is brought near the pith ball, electrons on the latter are pushed away to the opposite side of the ball. A shortage of electrons develops on the near side of the pith ball. Because the electrons on the rod repel the excess electrons on the far side of the pith ball, the ball is repelled from the rod.
D) When the rod is brought near the pith ball, electrons on the latter are pushed away to the opposite side of the ball. A shortage of electrons develops on the near side of the pith ball. Because the oppositely-charged near side is closer than the like-charged far side of the pith ball, it is attracted to the rod.
The pith ball is attracted to the rod because of the mechanism desribed above. Once the pith ball touches, excess charge transfers to the ball and it is repelled from the rod.
E) When the rod is brought near the pith ball, electrons on the latter remain unaffected. Because the electrons on the rod repel the electrons on the pith ball, the ball is repelled from the rod.
___2) In lecture we saw a demonstration about electricity that looked like the following:
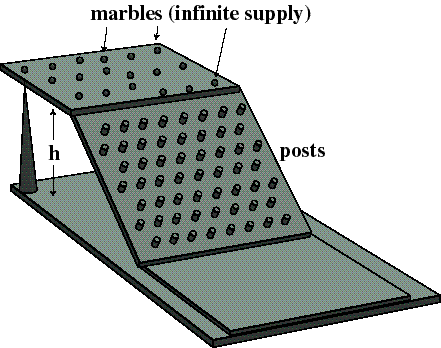
Which of the following statements, which describe a part of the analogy between marbles running down the face through the posts and current flowing through a light bulb element, is NOT true?
A) The marbles represent electrons, and their "flowing" across the device represents current.
B) The marbles colliding with the posts represents electron-atom collisions in the light bulb element.
C) The height of the upper platform, h, is analogously related to the resistance of the light bulb element. This doesn't make sense. See B) and E) for ideas about resistance.
D) The vibrating posts represent the thermal energy that causes light to emit from the element.
E) The marbles scattering randomly as they hit the posts represents how electrons lose kinetic energy as they move through the light bulb element.
This time Professor I.M. Dizzy had just left her laboratory in a hurry after finishing a series of experiments, when she slipped on a kiwi peel and hit the floor hard, causing temporary amnesia and terminal ridiculousness. She had undertaken the experiments to examine the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. Professor Dizzy was rushing to finish her experiment so she only had time to make graphs of her results, plotting a "curve" for each result on the same set of axes. She didn't take time to label the curves, nor the axes. You, as her assistant, now must help her determine the meaning of the different curves.
___3) Which of the following curves could correspond to a plot of voltage vs. current when resistance is held constant? Curve must go through origin and be linear, increasing.
(A) curve A?(B) curve B?(C) curve C?(D) curve D,?(E) none of these curves.
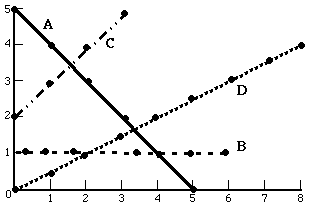
___4) Which curve above would correspond to a plot of current vs. resistance with voltage held fixed? Curve would asymptotically approach both axes, looks like an upside-down boomerang
(A) curve A (B) curve B (C) curve C (D) curve D, (E) none of these curves.
__5) The magnetic field lines for the bar magnet shown below represent:
The lines show the direction (arrows & direction) and magnitude (density of lines) of a force on the north pole of a test magnet.
(Sorry, drew the image by hand)
A) The direction an electron would move if it were placed near the magnet.
B) The magnitude & direction of the force on a proton placed near the magnet.
C) The direction and magnitude of the force on a paper clip placed near the magnet.
D) The direction and magnitude of the force on the north pole of another magnet placed near the magnet.
E) The location of various equipotential lines for the magnet.
__6) Which of the following is NOT important when generating a current in a coil of wire using a magnet?
A) The speed at which the magnet moves relative to the coil of wire.
B) The direction the magnet moves in relation to a coil of wire.
C) That the coil of wire is connected to a complete circuit.
D) The orientation of the magnet relative to the coil of wire.
E) All of the above are important when generating current using a magnet.
__7) Which of the following diagrams properly shows the electric field lines (for a positive charge) for the globe of a positively charged Van de Graaf generator.
D) showed field lines emmanating straight outwards from the sphere of the Van de Graaf. The lines show the direction of force on a positive test charge, hence the arrows would point outwards from the sphere.
__8) You have a positively-charged Van de Graaf generator; a small, positively charged pith ball; and a way to push the pith ball around. You wish to undertake an experiment to determine the voltage (potential energy difference) between two points on a line pointing towards the generator. Which of the following experiment procedures would NOT be necessary to determine this voltage?
(again, drew the image by hand)
A) A procedure to measure the charge on the pith ball
B) A procedure to measure the size of the pith ball. Not important.
C) A procedure to measure the force necessary to push the charge from one point to the other.
D) A procedure to measure the distance between the two points.
E) All of the above procedures are necessary to measure the voltage between the two points.
__9) Which of the following is the most common carrier of positive charge in everyday life?
A) "Holes," the places where electrons should be, but aren't.
B) Protons, which make up the nuclei of atoms. Too heavy, don't move.
C) Neutrons, which make up the nuclei of atoms. They don't have charge.
D) "Holes," the place where two electrons are in place of one. Bad definition of holes.
E) Ions, the packets of electrons that orbit nuclei of atoms together. Bad definition.
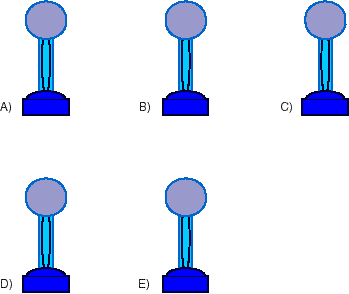
__10) In lecture we undertook experiments by analogy using a device like the following. For our experiments with this device, which property corresponded to voltage (which is the same as potential energy difference)?
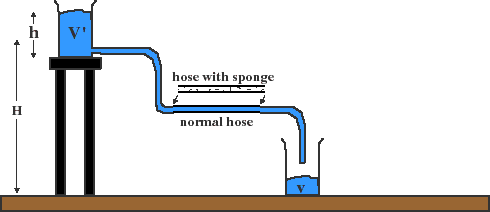
A) The amount of sponge stuck in the tubing.
B) The height of the blue fluid in the upper container. Corresponds to pressure on fluid.
C) The time it took for a fixed amount of blue fluid to empty into the lower container.
D) The amount of blue fluid per time that emptied into the lower container.
E) The difference in height between the upper and lower container.
__11) You have a wire and various means of pushing current through the wire. You want to make an electromagnetic (EM) wave to transmit information (as in a radio transmitter) through space. Which of the following do you absolutely need to do to make the EM wave?
A) Wrap the wire into a coil and place an iron rod at its center.
B) Push a direct current (DC) through the wire using a battery.
C) Place a bar magnet near the wire.
D) Push an alternating current (AC) through the wire. MUST be alternating in time.
E) Choose wire with the correct resistance.
__12) Which of the following graphs shows a wavelength of 10cm?
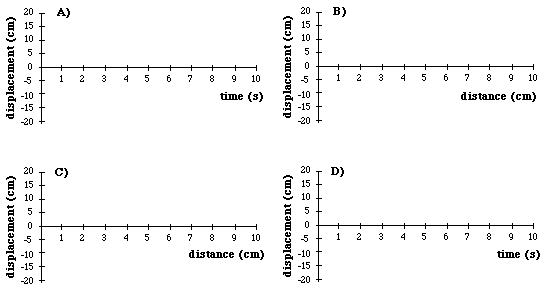
E) Both B) and C) show a wavlength of 10cm Both showed a complete cycle of length 10 cm. Curves A) and D) are plotted against time.
__13) You are attending a concert by your favorite oboe rock band. You know that the ten oboes make sounds according to the length of each oboe, which can be adjusted by different fingerings. Suddenly, while all the musicians are playing a long note, a madman runs onto the stage and releases nitrogen gas, which immediately displaces the air inside the oboes. Which of the following correctly describes the chaos that ensues?
A) The oboes suddenly sound different. The wavelength of the waves and their frequencies have changed.
B) The oboes suddenly sound different. The frequency of the waves and the sound wave speed have changed. Speed of sound is different for nitrogen gas. Wavelength is determined by the instrument, doesn't change. So frequency must change.
C) The oboes suddenly sound different. The wavelength of the waves and the sound wave speed have changed.
D) The oboes suddenly sound different. The weight of the gas in the oboes is heavier and so their music sounds more like heavy metal.
E) The oboes suddenly sound different. The frequency of the waves, their wavelengths, and the sound wave speed have all changed.
__14) The difference between a microwave and a light wave is:
A) Only the microwave involves changing electric and magnetic fields.
B) Light waves travel much faster through air.
C) The frequency of a light wave is much higher than that of a microwave.
D) Microwaves require atmosphere to travel through.
E) Microwaves only come from microwave ovens.
__15) Which of the following phenomenon does NOT involve EM radiation?
A) The propagation of visible radiation from the sun to the Earth.
B) Warming yourself by standing near a functioning wood stove.
C) Listening to a physics instructor tell you about global warming. Involves sound waves.
D) Listening to a physics instructor tell you about global warming over the radio.
E) Having your arm x-rayed at the doctor’s office.