|
 |
 |
 |
 | The srModel structure defines the slowness model used for ray tracing. The model can be either isotropic or anisotropic and it can include interfaces.
The slowness model is defined at nodal locations in three-dimensions, srModel.u(nx,ny,nz). To include topographic effects, the columns of the slowness model are sheared vertically. A typical grid spacing for active source work is 200 m in all directions. Also, see note on uneven grid spacing.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Example of Matlab display:
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | srModel =
u: [101x461x46 double]
anis_fraction: [101x461x46 double]
anis_theta: [101x461x46 double]
anis_phi: [101x461x46 double]
ghead: [-25 -115 101 461 46 0.5 0.5 0.2]
description: ‘hpt version of 082152_u5_plug_1dm_m12_6p converted’
filename: ‘/Users/drt/Projects/Undershoot/Skew/srInput/srModel_082152_u5_plug_1dm_m12_6p.mat’
nx: 101
ny: 461
nz: 46
gx: 0.5
gy: 0.5
gz: 0.2
nodes: 2141806
xg: [101x1 double]
yg: [461x1 double]
zg: [46x1 double]
maxx: 25
minx: -25
maxy: 115
miny: -115
maxz: 0
minz: -9
LON: [101x461 double]
LAT: [101x461 double]
elevation: [101x461 double]
srGeometry: [1x1 struct]
interface: [1x1 struct]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | srModel =
u: [284x208x71 double]
ghead: [0 0 284 208 71 0.05 0.05 0.05]
xg: [284x1 double]
yg: [208x1 double]
zg: [71x1 double]
anis_fraction: []
anis_theta: []
anis_phi: []
filename: ‘srModel_VISO_SM2_z50m_phaseB.mat’
nx: 284
ny: 208
nz: 71
gx: 0.05
gy: 0.05
gz: 0.05
nodes: 4194112
maxx: 14.15
minx: 0
maxy: 10.35
miny: 0
maxz: 0
minz: -3.5
EASTING: [284x208 double]
NORTHING: [284x208 double]
elevation: [284x208 double]
srGeometry: [1x1 struct]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
srModel.u
|
sec/km
|
Isotropic slowness
|
srModel.ghead
|
srModel.ghead(1)
|
km
|
X-offset of u(1,1,:) wrt origin cartesian system
|
See Coordinate System
|
srModel.ghead(2)
|
km
|
Y-offset of u(1,1,:) wrt origin of cartesian system
|
See Coordinate System
|
srModel.ghead(3)
|
integer
|
Number of nodes in the x-direction
|
also srModel.nx
|
srModel.ghead(4)
|
integer
|
Number of nodes in the y-direction
|
also srModel.ny
|
srModel.ghead(5)
|
integer
|
Number of nodes in the z-direction
|
also srModel.nz
|
srModel.ghead(6)
|
km
|
Spacing of nodes in the x-direction
|
also srModel.gx
|
srModel.ghead(7)
|
km
|
Spacing of nodes in the y-direction
|
also srModel.gy
|
srModel.ghead(8)
|
km
|
Spacing of nodes in the z-direction
|
also srModel.gz
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Derived Fields: Generic Set
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | There are number of derived fields for the srModel structure. The ones defined in the generic set are present for all models, whether or not water-path corrections are applied or other optional fields are used. Some of these may take up memory, so carrying them around to all functions might not be advised. Fields can be removed using the rmfield command.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
srModel.nx
srModel.ny
srModel.nz
|
integer
|
srModel.ghead(3:5)
|
srModel.gx
srModel.gy
srModel.gz
|
km
|
srModel.ghead(6:8)
|
srModel.nodes
|
integer
|
Total number of nodes (nx*ny*nz)
|
srModel.xg
srModel.yg
srModel.zg
|
km
|
Vectors storing x y and z values of nodes. Elevation is not included in these values; z value is model z-value as described in coordinate system.
srModel.zg is relative to top surface of velocity model; z is positive upward.
Matlab command:
srModel.xg=linspace(srModel.ghead(1), srModel.ghead(1)+ (srModel.nx(1)*srModel.gx,srModel.nx)’;
|
srModel.XG
srModel.YG
|
km
|
Matrix of x and y graph locations. See meshgrid in matlab.
|
srModel.LON
srModel.LAT
|
decimal degrees
|
Matrix of longitude and latitude positions that define the location of vertical columns of srModel.u
|
srModel.elevation
|
kilometers
|
Elevation to top layer of nodes that define the slowness model.
Can be plotted:
cartesian coordinates:
pcolor(srModel.xg, srModel.yg, srModel.elevation)
geographic coordinates: pcolor(srModel.LON,srModel.LAT,srModel.elevation)
|
minx, maxx
miny, maxy
minz, maxz
|
km
|
xyz limits of slowness graph in cartesian coordinate system
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Derived Fields: Waterpath Corrections
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | When waterpath corrections are required for airgun data (see the srControl structure), the function load_srModel derives a “seafloor” interface field and includes it in srModel. This is a derived sub-structure of srModel, i.e., let the code fill it in. The seafloor interface is derived from srElevation.
srModel.interface.id
|
integer
|
Unique interface id
|
srModel.interface.name
|
character (cell array)
|
{‘seafloor’ } (NOTE: must be cell array)
|
srModel.interface.X
|
km
|
Array of x-locations of grid points defining interface. Size of X and Y must be identical.
|
srModel.interface.Y
|
km
|
Array of y-locations of grid points defining interface. Size of X and Y must be identical.
|
srModel.interface.elevation
|
km
|
Elevation of seafloor at XY array locations
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
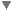  | Optional Fields: Anisotropy
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
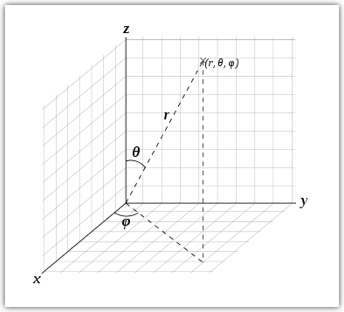
 | Anisotropy at a node is defined in spherical coordinates (r, θ, φ) where r is the percentage of anisotropy, θ is the zenith angle from the positive z-axis to the point, and φ is the azimuth angle from the positive x-axis to the orthogonal projection of the point in the x-y plane; see figure below.
If your model is isotropic (and srControl.tf_anisotropy=0), there is no need to define these fields.
srModel.anis_fraction
|
unitless
|
Fraction of anisotropy (e.g., 0.06 is 6%)
|
srModel.anis_theta
|
radians
|
θ is the zenith angle from the +z axis to the point; see figure.
|
srModel.anis_phi
|
radians
|
φ is the azimuth angle from the positive x-axis to the orthogonal projection of the point in the x-y plane. Positive φ is in the +x, +y direction.
|
srModel.anis_A
|
unitless
|
Scale term for azimuthal anisotropy. See Eqn. A1 of Dunn et al., 2005
|
srModel.anis_B
|
unitless
|
Scale term for azimuthal anisotropy. See Eqn. A1 of Dunn et al., 2005
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Optional Fields: Interface(s)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | Interfaces can be included in the velocity model allowing analysis of secondary arrivals (e.g., PmP). An interface is an optional field, meaning that it must be defined by the user. Note that the seafloor interface used for waterpath corrections is a derived field, not an optional field. The seafloor interace is discussed above (Derived Fields: Waterpath corrections).
srModel.interface.id
|
integer
|
Unique interface id.
|
srModel.interface.name
|
character (cell array)
|
Name of the interface causing either reflection or conversion. NOTE: Must be cell array, e.g. {‘Moho’}.
|
srModel.interface.X
|
km
|
2D matrix specifying x points at which the Z data is given. Size of X, Y, Z must be identical. Defined in local cartesian coordinates.
|
srModel.interface.Y
|
km
|
2D matrix specifying y points at which the Z data is given. Size of X, Y, Z must be identical. Defined in local cartesian coordinates.
|
srModel.interface.Z
|
km
|
The model z-value of the interface at the points in matrices X and Y. Defined in local cartesian coordinates.
|
srModel.interface.elevation
|
km
|
Elevation of the interface at the points in matrices X and Y.
|
srModel.interface(1)
id: 1
name: {‘moho’}
X: [551x141 double]
Y: [551x141 double]
Z: [551x141 double]
elevation: [551x141 double]
indiceAbove: [77691x1 double]
indiceBelow: [77691x1 double]
Normalx: [551x141 double]
Normaly: [551x141 double]
Normalz: [551x141 double]srModel.interface(1) =
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Derived Fields: Interface(s)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | Several derived fields are useful for calculating partial derivatives
srModel.interface.indiceAbove
|
integer
|
Nodal indice above the interface at (i,j) location
|
srModel.interface.indiceBelow
|
integer
|
Nodal indice below the interface at (i,j) location
|
srModel.interface.Normalx
|
unitless
|
Component of unit vector normal to the interface at (i,j) location
|
srModel.interface.Normaly
|
unitless
|
Component of unit vector normal to the interface at (i,j) location
|
srModel.interface.Normalz
|
unitless
|
Component of unit vector normal to the interface at (i,j) location
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  | Notes on Converting an old/hpt model to the new/stingray model
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | The definition of anisotropy in Stingray differs from hpt (theta and phi are switched in hpt and not consistent with conventional notation).
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | oldmodel =
mantle_vel: 7.7900
ghead: [-25 -65 0 0 0 0 111 271 51 0.5000 0.5000 0.2000]
a_t: [51x1 double]
a_p: 1.5708
a_r: [1534131x1 double]
moho: [136x56 double]
mhead: [-25 -65 56 136 1 1]
u: [1534131x1 double]
a_t: azimuth of anisotropy (-10˚ for EPR, e.g., indicated a CCW rotation of 10˚ wrt the x-axis) (will become phi)
a_p: this was the dip of the anisotropy (will become theta)
a_r: magnitude of anisotropy
|
 |
 |
|
 |