
The best way to determine the R-value of a specified material is to use a device that can induce a heat flow through that material and measure the temperature difference. Such an arrangement is called a Guarded Hotbox. Without the equipment to measure heat flow directly, we used the apparatus as a comparative tool.
Realizing that even the most advanced Hotbox in the world has a margin of error of +/- 4%, we decided to build a Calibrated Semi-Guarded Hotbox. (House Builder’s Update) Due to uncontrollable experimental errors such as the edge effect, thermal conductance and convection currents, we will test several insulation materials with known R-values and calibrate our data accordingly. A ratio of the heat difference between inside and outside temperatures of the box will allow us to calibrate our tests to known R-value material. In this case we will to use conventional Fiberglass Batt insulation. (ASTM)
A hot box is simply a device that holds a steady state temperature in a space directly adjacent to the material to be measured: the specimen sample. Heat flows through the material and its difference is measured on the outermost specimen chamber face.
Hobo data loggers will be placed in the “metering box” and on the outermost face of the specimen chamber. Readings will be made on several corresponding locations of the face with the Hobo, then averaged. A Raytech device will be used to validate the accuracy of the Hobo Dataloggers.
Methodology
First “Hotbox” Iteration
Negotiating Connections
Semi-Guarded Hotbox to be built
construction-2.JPG
construction-7.JPG
construction-8.JPG
construction-9.JPG
construction-10.JPG
insulation testing-25.JPG
insulation testing-11.JPG
insulation testing-7.JPG
insulation testing-1.JPG
insulation testing-26.JPG
insulation testing-2.JPG
insulation testing-22.JPG
insulation testing-15.JPG
insulation testing-20.JPG
insulation testing-27.JPG
insulation testing-3.JPG
bag testing feb.4-6.JPG
bag testing feb.4-16.JPG
bag testing feb.4-5.JPG
bag testing feb.4-21.JPG
bag testing feb.4-22.JPG
bag testing feb.4-10.JPG

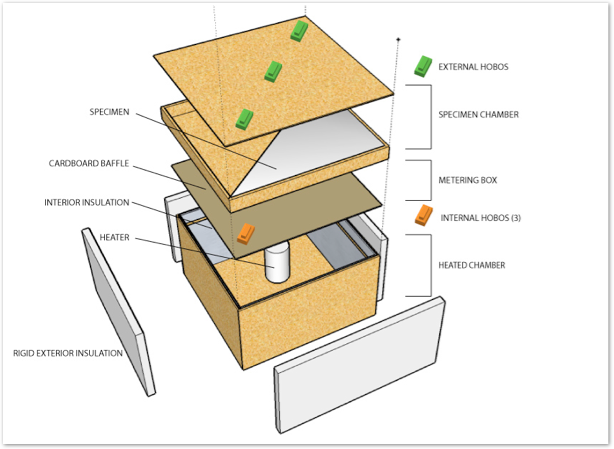
Diagram of Our Box click to enlarge
Construction and Testing