Astronomy 121
Examination 2
Questions -- Select the most correct answer
1. The geocentric theory for the Solar System can not
explain
a. retrograde motion
b. the motion of the Sun along the ecliptic
c. the motion of the Moon
* d. an observed annual stellar parallax
e. the daily rising and setting of the stars
2. Suppose that I have two objects, one of mass, M, and the other
of mass, m and that they are separated by a distance of 5 meters.
If I then move them apart so that they are separated by a distance of
15 meters, what happens to the strength
of the gravitational force between the two objects?
a. It becomes three times stronger
b. It becomes three times weaker
c. It becomes nine times stronger
* d. It becomes nine times weaker
e. The force of gravity is universal; it does not change.
Kepler's 3 laws of planetary motions are:
I. Law of Ellipses
II. Law of Equal Areas
III. Harmonic Law
3. The notion that a planet in a particular orbit travels fastest when
it is closest to the Sun is embodied in
a. Law I
* b. Law II
c. Law III
4. Which one of Kepler's laws of planetary motion could be restated as the
law of the Conservation of Angular Momentum?
a. Law I
* b. Law II
c. Law III
5. In non-mathematical terms, Kepler's third law says that
a. a planet moves more rapidly when near the Sun than when farther
away
* b. planets close to the Sun have shorter periods than those farther
away
c. the Sun is at the center of planetary orbits
d. slowly moving planets are close to the Sun
6. Which of the following is not a property associated with
planetary motions?
a. All planets orbit around the Sun in the same direction
* b. All planets orbit around the Sun roughly in the celestial equator
c. All planets have roughly circular orbits
d. All planets have elliptical orbits
7. A feature common to all of the Jovian planets is that
a. they are all composed primarily of icy material
b. they are all larger than or around the size of Juptier
* c. they all have ring systems
d. they are all heavily cratered
8. The Sun is composed primarily of
* a. hydrogen
b. helium
c. carbon
d. oxygen
e. iron
9. Which of the following facts must any theory for the formation of
the Solar System explain?
a. the orbital properties of the planets
b. the existence of three general classes of planets
c. the general rotational properties of the planets
d. the chemical composition of the Jovian planets
* e. It should be able to explain all of the above facts
10. There is strong evidence that, in the past, there was running water
on
a. Mercury
b. Venus
* c. Mars
d. the Moon
e. Jupiter
11. The first great observational astronomer was
a. Aristotle
b. Nicolaus Copernicus
* c. Tycho Brahe
d. Johannes Kepler
e. Issac Newton
12. The heliocentric theory for the Solar System was first
proposed by
a. Aristotle
* b. Aristarchus
c. Ptolemy
d. Copernicus
e. Galileo
13. According to Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
a. two objects attract each other according to their electrical
charge
b. two objects will attract or repel each other depending upon their
separation
* c. two objects will each attract other more strongly if they are moved
closer together
d. the attraction between two objects is stronger the less massive
they are
14. The momentum is a measure of an object's
a. mass
b. spin rate
* c. motion
d. electrical charge
15. The fact that the escape velocity from the Moon is less than that
from the Earth is due primarily to
a. the Moon's distance from the Earth
* b. the smaller mass of the Moon
c. the smaller diameter of the Moon
d. the higher temperature of the Moon
e. the shape of the Moon's orbit about the Earth
16. Which planet's physical and orbital characteristics differs the
most from all the other planets?
a. Mercury
b. Earth
c. Uranus
* d. Pluto
e. Jupiter
17. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the
Terrestrial planets?
a. high density
b. they have solid outer layers (hard surfaces)
c. they are small
* d. they are very far from the Sun (a > 10 A.U.)
e. they do not have ring systems
18. The chemical composition of the atmospheres of the Jovian planets is
most similar
* a. to that of the Sun
b. to that of Venus
c. to that of the Earth
d. to that of the Moon
e. to that of Pluto
19. Which of the following is a characteristic of the Jovian
planets?
a. small size
b. high density
* c. composed primarily of hydrogen and helium
d. no satellite systems
e. hard surfaces
20. The temperature of a gas is a measure of
a. the masses of the particles which make up the gas
* b. the average speed at which the gas particles move
c. the average gravitational force each gas particle feels
d. the density of the gas particles
21. If an object were abundant in refractory elements but had few
volatile elements, which of the following is the most likely
(simplest) explanation?
a. the object was formed in a region of low temperature
* b. the object was formed in a region of high temperature
c. the object was formed in a region which was first hot,
then cold, then hot, and then cold again
d. the object was formed in the Sun and then ejected into the
Solar System
22. Planetesimals are usually composed of
a. gaseous hydrogen or helium or a combination of them
* b. rock, ice or combinations of rock and ice
c. rock, iron, helium, or combinations of them
d. ice
e. rock
23. Comets are thought to have formed
a. in the Oort Cloud where they are found today
b. in the inner Solar System where radiation pressure pushed out to
the Oort Cloud
* c. in the vicinity of Uranus and Neptune from where interactions
with the Jovian planets moved them out to the Oort Cloud
d. in interstellar space (outside of the Solar System) after which
the Sun captured them
24. What important event occurred while the Sun was in its T Tauri
phase (the phase when the young Sun developed an intense Solar Wind)?
a. Jupiter was formed
b. the Earth-Moon system was formed
c. the Sun ran out of fuel and started to fade
* d. the gas remaining in the Solar System was blown out
25. The density of the Moon is most similar to
a. the density of the Sun
b. the density of Jupiter
c. the density of the center of the Earth
* d. the density of the rocks in the crust of the Earth
e. the density of Pluto
26. The currently accepted theory for the origin of the Moon
a. proposes that the young Earth spun rapidly and ejected the Moon
from its surface
b. proposes that the Moon was formed outside of the Solar System
and was subsequently captured by the Sun
* c. proposes that the young Earth was struck by a Mars-sized object
which led to the formation of the Moon
d. proposes that Earth and Moon formed independently but from one
collapsing gas cloud
27. Terrestrial planets are formed from the coalescence of
a. asteroids
b. gases in the Solar Nebula
* c. planetesimals
d. minor bodies, such as comets
e. small objects, such as moons
28. The primary characteristic of the environment in which the planets
form which accounts fort the gross differences between the classes of planets is
* a. the temperature
b. the chemical composition
c. the orbital speed at that position
d. the amount of hydrogen
e. the mass
29. The asteroids are thought to be
a. a Terrestrial planet which was broken-up during a close encounter with
Saturn
b. small objects formed outside of the Solar System which were
subsequently captured
c. comets which were trapped in the inner Solar System by the
Earth
* d. planet-building material which Jupiter did not allow to form
into a planet
e. the largest moon of Mars which was destroyed during a close
encounter with Jupiter
30. A key to understanding why there is a large difference between
the Jovian planets and the Terrestrial planets is
* a. that water was able to exist in solid form (ice) around the the
orbits of the Jovian planets
b. the fact that the outer Solar System contains more hydrogen
than the inner Solar System
c. the ability of rocky material to be in solid form only around
the orbits of the Jovian planets
d. that there was no gas in the inner Solar System
e. we do not understand why the Jovian planets are so different
from the Terrestrial planets
31. Most of the mass of the Solar System is contained in
* a. the Sun
b. the Earth
c. Jupiter
d. the asteroids
e. the comets
32. Which of the following planets has a ring system?
a. Jupiter
b. Saturn
c. Uranus
d. Neptune
* e. All of the above planets have ring systems
33. Newton's second law of motion, which requires that the acceleration of
the Earth is much greater than the acceleration experienced by the Sun
due to the mutual gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Sun,
strongly supports the Copernican belief that
* a. the Earth orbits the Sun
b. the Universe is very large
c. the daily motion of celestial bodies results from the Earth's
rotation on its axis
d. planetary orbits are circular in shape
34. Compared to the Jovian planets, on the average, Terrestrial planets
are
a. more dense and more massive
b. less dense and more massive
* c. more dense and less massive
d. less dense and less massive
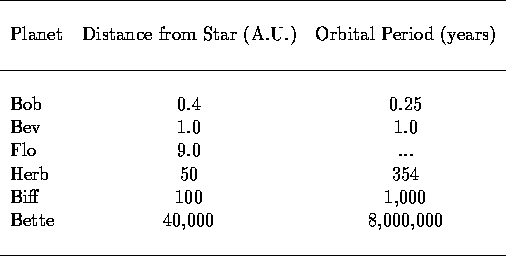
Questions 35 - 40 refer to the TABLE below in which the
orbital properties of the objects in a hypothetical
solar system are listed.
The star in this solar system has precisely the same properties as that of our
Sun and the solar system formed from an interstellar cloud which had the
same chemical composition as the interstellar cloud from which our Solar
System formed.
35. Which of the following is most likely to be composed of
roughly equal amounts of rocky and icy material?
a. Bev
b. Bob
c. Flo
* d. Biff
36. Of the following, the least massive object is most likely to be
a. Bob
b. Bev
c. Flo
d. Herb
* e. Bette
37. Of the following, which is probably the most massive
object?
a. Bev
b. Bob
* c. Flo
d. Bette
e. Biff
38. What is the orbital period of Flo?
a. 1 year
b. 9 years
* c. 27 years
d. 1,000 years
e. 10,000,000 years
39. Bette is probably
a. a rocky planet
b. a gas planet
c. an icy planet
d. an asteroid
* e. in actuality, a comet
40. Of the following, the planet with the highest density is most
likely
* a. Bev
b. Flo
c. Herb
d. Biff
e. Bette