I did not go over the sample exam very closely. The final exam for the class will
consist of multiple choice questions and short answer questions. The
sample exam shown below consists of only multiple choice questions.
1. There was a total Lunar eclipse on January 9, 2001.
What was the rough phase of the Moon on January 30, 2001?
a. new
* b. first quarter
c. waxing gibbous
d. full
e. third quarter
2. Of the following dates, for an observer in Santiago, Chile
(lat=30 degrees South), the day with the greatest number of hours
of daylight is
a. March 21
b. June 21
c. September 21
* d. December 21
3. The diurnal path of the Sun is best described as
a. a circle centered on the zenith of the observer.
b. the ecliptic.
* c. a circle centered on the North Celestial Pole.
d. an ellipse.
e. an ellipse centered on the zenith of the observer.
4. The solar day is  than the sidereal day because
than the sidereal day because 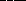
a. shorter; the Earth's rotation period is increasing.
b. longer; the rotation axis of the Earth is slowly precessing.
c. shorter; the Earth orbits around the Sun.
d. longer; the Earth's rotation period is increasing.
* e. longer; the Earth orbits around the Sun.
5. The tropical year is 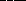 than the
sidereal year because
than the
sidereal year because 
a. longer; of precession.
* b. shorter; of precession.
c. longer; of tidal forces due to Jupiter.
d. shorter; of tidal forces due to Jupiter.
e. longer; of the strong winds found at mid-northern latitudes.
6. Venus rotates in the clockwise sense as viewed from the North Celestial
Pole while it orbits about the Sun in the counter-clockwise sense.
Which of the following statements about Venus is true?
* a. The stars rise in the west and set in the east.
b. The solar day is longer than the sidereal day.
c. The annual motion of the Sun through the stars is
east to west.
d. The diurnal motions are centered on the observer's zenith.
e. All of the above are correct statements.
7. The annual variation in the position of celestial objects is caused by
* a. the Earth's revolution about the Sun.
b. the Earth's rotation on its axis.
c. the motion of the Moon about the Earth.
d. the precession of the Earth's axis of rotation.
8. The first person to propose a heliocentric theory for the Solar
System was
a. Erastosthenes
* b. Aristarchus
c. Aristotle
d. Copernicus
e. Kepler and Galileo proposed ones at around the same time
9. Where on the Earth are no stars circumpolar?
a. at the North Pole
b. in a small region around Eugene, OR
* c. on the equator
d. anywhere in a small region the size of Ohio centered
on the North Pole
e. anywhere in a small band the size of California around the
equator
10. Where must an observer be located on the Earth if she sees only half
of the entire sky over the course of a year?
* a. the North Pole
b. Eugene, OR (or near Eugene, OR)
c. the equator
d. near Santiago, Chile
11. You notice that on December 21, the Sun reaches a maximum
altitude above the horizon of 22.5 degrees. What is your latitude?
a. lat = 90 ; you are at the North Pole
; you are at the North Pole
b. lat = 69.5 ; you are near the Arctic Circle
; you are near the Arctic Circle
* c. lat = 44 ; you are in Eugene, OR
; you are in Eugene, OR
d. lat = 23.5 ; you are near the Tropical Zone
; you are near the Tropical Zone
e. lat = -90 ; you are at the South Pole
; you are at the South Pole
12. Eclipses seasons occur roughly 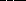 because
because 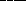
a. every month; the Moon is always in the ecliptic plane
b. every 18 years; the Moon's orbit is tilted 5 with respect to the ecliptic plane
with respect to the ecliptic plane
* c. every 6 months; the Earth's axis is tilted with respect to the ecliptic plane
d. every month; the Moon's orbit is never in the ecliptic plane
e. every 6 months; the Moon's orbit is tilted 5 with respect to the ecliptic plane
with respect to the ecliptic plane
13. Yesterday, I went outside and saw star Z rise at precisely 10:00 p.m.
When did star Z rise three nights ago?
* a. before 10:00 p.m.
b. at precisely 10:00 p.m.
c. after 10:00 p.m.
d. can't say when star Z rose because of precession
14. On the summer solstice, the Sun
a. reaches its farthest point south of the Celestial equator
b. crosses the Celestial equator moving northward
* c. reaches its highest point north of the Celestial equator
d. crosses the Celestial equator moving southward
e. the Sun's position on the Celestial Sphere depends upon what
hemisphere you are in
15. The assumption that the stars are fixed firmly to the Celestial
Sphere turns out to be reasonable because
a. stars are, in fact, stationary; they do not move
b. stars move very slowly compared to planets; speeds much
less than 1 mile per hour
c. any observed stellar parallax is really just an optical
illusion
d. stars are fairly nearby
* e. stars are extremely distant
16. Suppose you live on the equator. You go out and see the
first quarter moon and it is rising. Roughly, what time is it?
* a. noon
b. sunset
c. midnight
d. sunrise
e. around 9 pm
17. Suppose you are standing on the Moon. You see a new Earth.
What is the phase of the Moon?
a. New
b. First Quarter
* c. Full
d. Third Quarter
e. Gibbous
18. The seasons in the northern hemisphere are caused by
a. the varying hours of daylight over the course of a year
b. the variation in how directly sunlight strikes
the mid-northern latitudes of the Earth
c. the Earth being closer to the Sun in June than in December
* d. a and b
e. a, b, and c
19. Suppose that you are on a strange planet. You notice that the
daily motion of the stars is around a fixed point
30 above the horizon. You deduce that your latitude on this
planet is
above the horizon. You deduce that your latitude on this
planet is
a. 0 degrees
* b. 30 degress
c. 44 degrees
d. 60 degrees
e. 90 degrees
20. In order for a solar eclipse to occur, the Moon must be
* a. near new Moon
b. near first quarter
c. near third quarter
d. near full Moon
e. in a retrograde loop
21. Which of the following statements is not correct?
a. planetary orbits are roughly circular in shape
b. planetary orbits are roughly in the ecliptic plane
c. all planets orbit about the Sun in the same sense (CCW as
viewed from the north)
* d. all planets rotate on their axes in the same sense (CCW as
viewed from the north)
e. All of the above are correct statements
22. Suppose that I have two objects, one of mass, M, and the other
of mass, m, and that they are separated by a distance of 5 meters.
If I then move them so that they are separated by a distance of 1 meter,
the strength of gravity between the
two objects 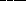 by
by 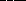 .
.
a. increases; five times
b. decreases; five times
* c. increases; twenty-five times
d. decreases; twenty-five times
e. decreases; four times
23. A feature common to all of the Jovian planets is that
* a. they have large magnetic fields compared to the Earth
b. they are all larger than or around the size of Juptier
c. they all have atmospheres composed primarily of methane
d. they all have many volcanoes
e. they all have large liquid metallic hydrogen layers in
their interiors
24. Which of the following facts must any theory for the formation of
the Solar System explain?
a. the orbital properties of the moons around Jupiter
* b. the existence of three general classes of planets
c. the general rotational properties of the moons of the
Terrestrial planets
d. the origin of the Kirkwood gaps
e. It must be able to explain all of the above facts
25. According to Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, if I double the
mass of one of the bodies, then
a. the two objects attract each other with a force which is
one-half as strong
b. the two objects attract each other with a force which is
four times as strong
* c. the two objects attract each other with a force which is
two times as strong
d. the two objects attract each other with a force which is
eight times as strong
e. There is no change -- gravity depends only on how far
apart the objects are
26. The fact that the escape velocity from the Moon is less than that
from the Earth means that
a. the Moon's distance from the Earth is large
b. the mass of the Moon is greater than that of the Earth
c. the Moon is smaller than the Earth
* d. you would weigh less on the Moon than on the Earth
e. the Moon can easily hold onto an atmosphere
27. Which of the following is not a general characteristic of the
Terrestrial planets?
a. iron/nickel cores
b. solid outer layers (hard surfaces)
c. high densities
* d. dense atmospheres
e. impact craters
28. Comets are thought to have formed
a. in the Oort Cloud where they are found today
b. in the inner Solar System where radiation pressure
pushed them out to the Oort Cloud
* c. in the vicinity of Uranus and Neptune from where
interactions with the Jovian planets moved them out
to the Oort Cloud
d. in interstellar space (outside of the Solar System)
after which the Sun captured them
29. The currently accepted theory for the origin of the Moon
a. proposes that the young Earth spun rapidly and ejected
the Moon from its surface
b. proposes that the Moon was formed outside of the Solar
System and was subsequently captured by the Sun
* c. proposes that the young Earth was struck by a Mars-sized
d. proposes that the Earth and Moon formed independently
but from one collapsing gas cloud
30. The asteroids are thought to be
a. a Terrestrial planet which was broken-up during a close
encounter with Saturn
b. small objects formed outside of the Solar System which were
subsequently captured
c. comets which were trapped in the inner Solar System by the
Earth
* d. planet-building material which Jupiter did not allow to
form into a planet
e. the largest moon of Mars which was destroyed during a
close encounter with Jupiter
31. A key to understanding why there is a large difference between
the Jovian planets and the Terrestrial planets is
* a. that water was able to exist in solid form (ice) around
the orbits of the Jovian planets
b. the fact that the outer Solar System contains more
hydrogen than the inner Solar System
c. the ability of rocky material to be in solid form only
around the orbits of the Jovian planets
d. that there was no gas in the inner Solar System
e. we do not understand why the Jovian planets are so
different from the Terrestrial planets
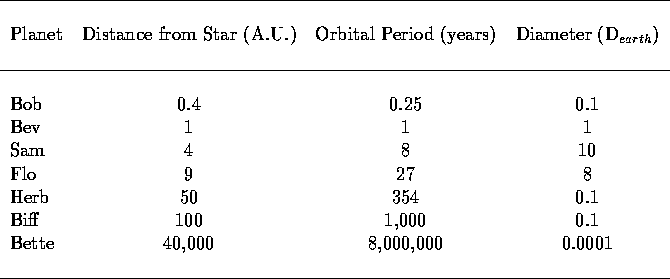
Questions 32 - 37 refer to the TABLE below in which the
orbital properties of the objects in a hypothetical
solar system are listed.
The star in this solar system has precisely the same properties as that of our
Sun and this solar system formed from an interstellar cloud which had the
same chemical composition as the interstellar cloud from which our Solar
System formed.
32. Which of the following most likely contains liquid metallic
hydrogen?
a. Bev
b. Bob
* c. Flo
d. Herb
33. Of the following, the least massive object is most likely to be
a. Bob
b. Bev
c. Flo
* d. Herb
34. Of the following, which is the most likely to have a ring system?
a. Bev
b. Bob
* c. Flo
d. Bette
35. Of the following, the most geologically active planet is likely to be
a. Bob
b. Biff
c. Sam
d. Flo
* e. Bev
36. Of the following, which is most likely to have the least massive
atmosphere?
* a. Bob
b. Bev
c. Sam
d. Flo
37. Of the following, which is most likely to have the largest
(in relation to its mass) iron/nickel core?
* a. Bev
b. Sam
c. Flo
d. Bette
e. Biff
The following figure
is a highly exagerrated representation of the orbit of the Earth.
Use the figure to answer questions 38 and 39.
38. At what letter is the Earth traveling the fastest in its orbit?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
e. E
39. At what letter is the length of the solar day the greatest? [Note
I do not mean the mean solar day which has a length of 24 hours.]
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
e. E
40. In a moment of rage you kick a wall. Subsequently, your foot hurts.
This is best explained by
a. Newton's first law of motion (the inertia law)
b. Newton's second law of motion (the force law)
* c. Newton's third law of motion (the reaction law)
d. Newton's law of universal gravitation
41. If a comet or a spacecraft passes nearby Jupiter and gains some energy
(i.e., it speeds up), what is the effect on Jupiter?
* a. Jupiter will revolve more quickly about the Sun
b. Jupiter will not suffer any affect due to this encounter
c. Jupiter will revolve more slowly about the Sun
42. Volatile elements are those which
a. take up large volumes in space
b. condense at high temperatures
* c. are easily vaporized
d. are difficult to vaporize
43. Terrestrial planets have different chemical compositions than Jovian
planets because
a. they formed in regions of the solar nebula which had
radically different chemical compositions
* b. of high temperatures in the inner solar system
c. Terrestrial planets are denser than the Jovian planets
d. Jovian planets have stronger magnetic fields
e. the many satellites of the Jovian planets modified the
planet's atmospheres
44. Planets are generally spherical because of
a. rotation
b. magnetic fields
* c. the nature of gravity
d. tidal forces due to the Sun
e. radioactive heating in their interiors
45. Which of the following is likely to have been the most important process
in the formation of Jupiter's primitive atmosphere?
a. vaporization of colliding comets
* b. gravitational capture of surrounding gases
c. capture of surrounding charged particles by its magnetic
field
d. respiration of living organisms
e. outgassing from its interior
46. Planetary circulation is driven by heat-driven convection and by the
planet's
a. magnetic field
* b. rotation
c. internal radioactive heating
d. tidal interactions with its satellites
47. The dark-colored regions on the Moon are known as the
a. highlands and are thought to be the youngest features on
the Moon
b. highlands and are heavily cratered
c. maria and are thought to be old; ages up to 4.6
billion years
* d. maria and are thought to be around 3.2 - 3.8 billion
years old
e. weird terrain
48. Which of the following Terrestrial planets shows strong evidence for
past or present volcanism?
a. Venus
b. Earth
c. Mars
d. the Earth and Venus show evidence for volcanism
* e. Venus, Earth, and Mars all show evidence of volcanism
49. Active geology on a planet
a. is due to the existence of a lithosphere
b. is due to a differentiated interior
c. requires that the planet have a moon
d. occurs in smaller planets, in general
* e. is due to a hot interior
50. Convective motions in the
a. lithosphere are thought to drive plate tectonics
* b. asthenosphere are thought to drive plate tectonics
c. mesosphere are thought to lead to differentiation
d. Earth's outer core are thought to drive plate tectonics
e. lithosphere are thought to produce differentiation
51. Which of the following describes the most likely planet to have an
atmosphere?
* a. large mass, small radius, low temperature
b. low mass, small radius, low temperature
c. large mass, large radius, high temperature
d. low mass, large radius, high temperature
e. large mass, large radius, low temperature
52. Which of the following statements about the surface of Venus is correct?
a. The surface of Venus is thought to be ancient;
4.6 billion years old
b. There is an overabundance of large craters with diameters
greater than 300 km on Venus
* c. The surface of Venus is fairly young; less 1 billion years
d. The surface of Venus is primarily highland regions
e. The largest volcanos in the Solar System are found on Venus
53. The current atmospheres of Venus, Earth, and Mars are thought
a. to be secondary atmospheres
b. to all contain carbon dioxide
c. to generate weather in their tropospheres
d. to be due to outgassing or to have been carried in by
comet-like objects
* e. All of the above are correct statements about the
atmospheres of the Terrestrial planets
54. The principal reason that the atmosphere of Venus has evolved so that its
current temperature is 900 F while the current temperature of the Earth
is only 50 - 60 F, is
a. Venus started with a pure CO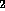 atmosphere while the
Earth started with significant amounts of
N
atmosphere while the
Earth started with significant amounts of
N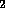 and O
and O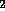 in addition to CO
in addition to CO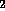 in its atmosphere
in its atmosphere
atmosphere
b. that the Earth shows vigorous plate tectonic activity
c. that life on Venus was never able to advance beyond
simple micro-organisms
* d. that liquid water could not exist on Venus
e. that Venus does not have an Ozone layer
55. The bulk of the carbon dioxide initially present in the atmosphere of
the young Earth
a. has been lost into space
b. is currently trapped in the high-altitude clouds around
the Earth
* c. is tied up in the crust of the Earth
d. is contained in the oceans of the Earth
e. is still contained in the atmosphere
56. The conditions in the current atmosphere of Mars are
a. such that water cannot exist in any form on or near the
surface of Mars
b. such that one expects a substantial layer of Ozone to form
c. such that liquid carbon dioxide can flow freely on Mars
* d. such that water can exist as a vapor near the surface of
Mars
e. such liquid water can flow freely on the surface of Mars
57. On Venus, most of the water
a. is tied up in large polar caps on the night side of the
planet
b. is tied up in the dense clouds which surround the planet
* c. has been lost to space after being broken apart by solar
radiation
d. has risen to high altitudes and forms a tenuous cloud
around Venus
e. is trapped in the oceans and crust of Venus
58. The Apollo landings showed there to be similar abundance ratios
for several isotopes of oxygen on the Earth and Moon; these
results argue against which theory of lunar formation?
a. fission theory
* b. capture theory
c. formation from the same cloud
d. impact theory for lunar formation
59. Maria are thought to have formed as
a. bodies of water which are now dried up
* b. lava flows
c. uplifted plains (highland regions)
d. areas eroded by wind before the Moon lost its atmosphere
60. Why is there no evidence of small impact craters (less than 1.4 km) on
Venus?
a. no objects of such size ever reached the surface due
to Venus's strong magnetic field
* b. the thick atmosphere burns up most objects which produce
craters of this size
c. small impact craters have been eroded by water and wind
d. the statement is incorrect -- there are many such small
craters on Venus
61. Neptune's atmosphere is composed primarily of
* a. hydrogen
b. helium
c. nitrogen
d. oxygen
e. methane
62. Near the core of Jupiter, hydrogen is
a. a low temperature molecular gas
b. a high temperature ionized gas
c. a solid
* d. a liquid metal
e. a liquid
63. How do we know what the internal structures of the Jovian planets
are like?
a. probes have been sent into the interiors of the Jovian
planets
b. astronomers have used the internal structure of the Earth
as a basis for comparison
c. astronomers examined the compositions of the satellites
of the planets
* d. astronomers used information about the physical
characterisitcs of the planets and the laws of physics to
deduce theoretical models
64. Very few heavy elements are observed in the atmosphere of Jupiter. Why
do you suppose that this is true?
a. They evaporated away
b. There were no heavy elements in the vicinity of Jupiter
when the Solar System formed
c. There are very many heavy elements, we just can't detect
them
* d. They have sunk to the center of Jupiter
65. The visible structure of Saturn's atmosphere is more muted than Jupiter's
visible structure because Saturn
a. does not have a strong magnetic field
b. does not have a volcanically active satellite as does
Jupiter (i.e., Io)
* c. has a thicker cloud layer (atmosphere)
d. has a layer of obscuring haze in its upper atmosphere
e. has a grossly different chemical composition compared to
Jupiter
66. The Great Red Spot on Jupiter rotates in the counter-clockwise
sense implying it is 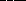 the surrounding atmosphere. The Great Red Spot is in the southern
hemisphere.
the surrounding atmosphere. The Great Red Spot is in the southern
hemisphere.
a. at a lower pressure than
* b. at a higher pressure than
c. at the same pressure as
67. The source of Jupiter's excess heat is thought to be
a. lightning bolts in its atmosphere
b. helium rain
* c. internal heat left over from its formation
d. absorption of some energy radiated by Saturn
e. recent impacts of asteroids and comets
68. The Roche limit for a large moon is the distance from a planet
a. beyond which the planet's gravitational tidal forces are
so strong that the moon could not have formed
b. at which tidal forces reach their maximum strength
* c. at which the planet's tidal forces become equal to the
gravitational force holding the moon together
d. beyond which only ring systems could form
69. Due to the Coriolis force, if I am just north of the equator of the Earth
and drop an object from the top of a tall tower, the object would fall
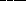 .
.
a. straight down
b. spiral downward in the couter-clockwise sense
* c. deflect to the east
d. spiral downward in the clockwise sense
70. The different colors of the belts and zones in Jupiter arise
because the clouds
* a. form at different heights
b. are composed of grossly different materials
c. are moving with different speeds
d. are slowly sinking
e. are slowly condensing
71. The fact that the circulation patterns on Saturn break apart into small
cells is due to
a. tidal forces
b. electrical forces
* c. conservation of angular momentum
d. conservation of energy
e. centrifugal force
72. The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is due to
a. volcanic activity below the cloud-tops
b. the interaction of the atmosphere with a tall mountain on
the surface of Jupiter
c. the infall of a large comet
* d. meteorological conditions in the atmosphere (i.e., a storm)
e. a region having a grossly different chemical composition
from the surrounding regions
73. Which of the following are responsible for maintaining thin rings such as
are found around Uranus and Neptune?
* a. shepherd satellites
b. magnetic fields
c. tidal forces
d. the solar wind
e. resonances with moons
74. The Cassini Gap in the rings of Saturn arises because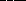
a. the particle orbits are chaotic there
* b. of a resonance with the orbit of the satellite Mimas
c. of tidal stresses due to Saturn
d. of the Roche limit
e. of the interaction with the magnetic field of Saturn
75. Which of the following statements about Uranus is true?
a. Uranus orbits about the Sun in the clock-wise sense as
viewed from the North
b. Uranus show a strong source of excess energy (like Jupiter)
* c. Uranus shows atmospheric circulation patterns similar to
those of Jupiter and Saturn
d. Uranus has a large liquid metallic hydrogen layer
e. All of the above are true.
76. Uranus and Neptune are much less massive than Jupiter and Saturn because
* a. the Sun turned-on before Uranus and Neptune
completed their formation process
b. the outer solar system was always depleted in hydrogen gas
c. tidal forces due to Jupiter disrupted their formation
processes
d. they are within the Roche limit of the Sun
e. they were formed outside of our solar system and were
subsequently captured
77. Planetesimals are expected to be composed partly of 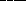 and partly of
and partly of 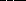 .
.
a. gas/ice
* b. ice/rock
c. rock/metal
d. liquid metallic hydrogen/liquid hydrogen
78. A particle in a ring would 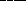 a shepherd
satellite outside the ring and it would
a shepherd
satellite outside the ring and it would
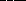 a shepherd satellite located inside the ring.
a shepherd satellite located inside the ring.
a. gain energy from; lose energy to
b. gain energy from; gain energy from
* c. lose energy to; gain energy from
d. lose energy to; lose energy to
79. If a comet orbits the Sun with a period of 64 years, what is the size of
its orbit?
a. 1 A. U.
b. 4 A. U.
c. 8 A. U.
* d. 16 A. U.
e. 64 A. U.
80. Suppose that the Earth formed around where Mars is today. Other than
this, the properties of the young Earth are unchanged. How might this
hypothetical Earth turn-out?
a. The atmosphere of the Earth would evolve to resemble
the current atmosphere of Mars.
b. There would be no possiblity of having liquid oceans
on the Earth today
* c. It is likely that the Earth would evolve to support an
atmosphere with liquid water, unlike the current Mars
d. The Earth would suffer a Runaway Greenhouse effect and
resemble Venus
e. The Earth would be tidally disrupted by Jupiter and would
no longer exist. Mars escaped this fate
because it is small.
 than the sidereal day because
than the sidereal day because 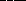
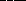 than the
sidereal year because
than the
sidereal year because 
 ; you are at the North Pole
; you are at the North Pole
 ; you are near the Arctic Circle
; you are near the Arctic Circle
 ; you are in Eugene, OR
; you are in Eugene, OR
 ; you are near the Tropical Zone
; you are near the Tropical Zone
 ; you are at the South Pole
; you are at the South Pole
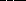 because
because 
 with respect to the ecliptic plane
with respect to the ecliptic plane
 with respect to the ecliptic plane
with respect to the ecliptic plane
 above the horizon. You deduce that your latitude on this
planet is
above the horizon. You deduce that your latitude on this
planet is
 by
by  .
.
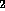 atmosphere while the
Earth started with significant amounts of
N
atmosphere while the
Earth started with significant amounts of
N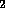 and O
and O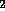 in addition to CO
in addition to CO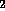 in its atmosphere
in its atmosphere
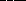 the surrounding atmosphere. The Great Red Spot is in the southern
hemisphere.
the surrounding atmosphere. The Great Red Spot is in the southern
hemisphere.
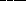 .
.
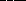
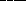 and partly of
and partly of 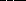 .
.
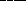 a shepherd
satellite outside the ring and it would
a shepherd
satellite outside the ring and it would
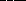 a shepherd satellite located inside the ring.
a shepherd satellite located inside the ring.