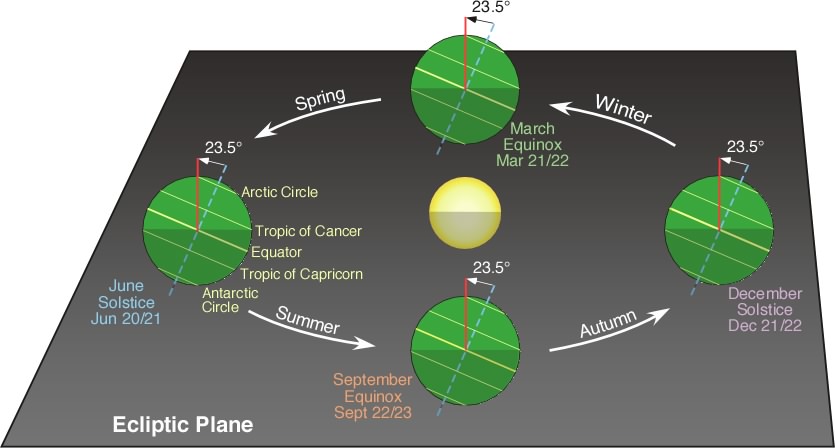
To define positions of objects on the Celestial Sphere, we use a system analogous to longitude and latitude. The rotation axis of the Earth and the orbital axis of the Earth are not parallel (they form an angle = 23.5o).

As a result, the Ecliptic and the Celestial Equator are inclined with respect to each other. Because of this, the Sun is sometimes above the Celestial Equator and sometimes below the Celestial Equator. This gives us some natural checkpoints on the sky (spheres have no ears to grab). We define the following points on the Celestial Sphere;
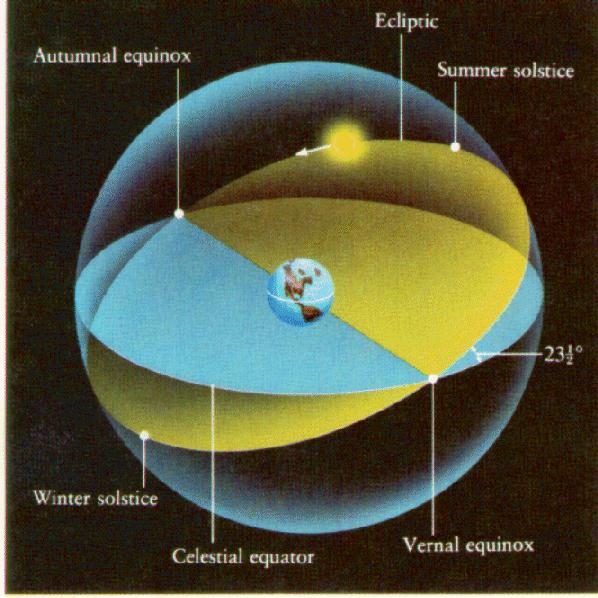
Vernal (Mar 20, 2021 UTC) and Autumnal (Sep 22, 2021 UTC) Equinoxes and Winter (Dec 21, 2021 UTC) and Summer (June 20, 2021 UTC) Solstices
The two equinoxes occur when the Sun passes through the Celestial Equator and the two solstices occur when the Sun is at its greatest distance north and south of the Celestial Equator.
The seasons change on a period of 365.2422 days (the Tropical year); an interval slightly shorter than the sidereal year. The cause of the changing of the seasons is the misalignment between the rotation axis and orbital axis of the Earth coupled with the orbital motion of the Earth. Huh? The question is then

The heating (angle), for a particular location, varies over the course of a year. This is the main effect.
|
|
On June 22 (or so), the Sun reaches its farthest point north of the Celestial Equator, the Summer Solstice. The Sun then moves toward the Celestial Equator, passing through the Celestial Equator on around September 22, the Autumnal Equinox. The Sun reaches its maximum distance south of the Celestial Equator on around December 22, the Winter Solstice, passing through the Celestial Equator, heading north, on around March 21, the Vernal Equinox.How do the diurnal circles for the Sun vary over a year in Eugene, OR (latitude ~ 44o N, longitude ~ 123o W). In Eugene, the altitude of the NCP above the north point on the horizon is ~ 44o. [ How far is the Celestial Equator above the south point on the horizon? Answer: ~ 46o.] So, what is the altitude of the Sun above the (South/North?) point on the horizon at roughly noon on the equinoxes and solstices?
So, in Eugene, the maximum altitude of the Sun above the horizon is:
The Arctic circle is the region on the Earth where the Sun can be above the Horizon for longer than 24 hours, i.e., where the Sun is circumpolar.
|
Consequently, further rules concerning leap years are formulated:
Unfortunately, this still isn't quite right and it was decreed that there would be no leap years for the years 4000, 8000, and so on.
