THE SOLAR SYSTEM
For the next six weeks we will concentrate on trying to understand how the
Solar System formed, how it has evolved since its formation, and
its place in the Universe. In this context, at some
point, we will address the questions of whether the Solar System
and life is unique
or whether there are other examples of these things in the
Universe. sidebar --
it is only within your lifetimes that most of the detailed
knowledge about the planets has become available. This is due primarily to
the space program. You were born in a good time for planetary research.
The Solar System is located in the grouping of stars (galaxy) known as
the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way is just one of many billions of
galaxies in the Universe. The Milky Way galaxy is a spiral
galaxy which contains roughly 100 billion stars and has a mass of roughly
10 - 100 billion M . The
visible material of the Milky Way is
contained in a thin rotating disk. The diameter of the disk is on
the order 100,000 - 300,000 light years (1 light year = 6 trillion
miles = 9.3 trillion kilometers)
and has a thickness of several thousands of light years. The
disk of the Milky Way is very thin.
. The
visible material of the Milky Way is
contained in a thin rotating disk. The diameter of the disk is on
the order 100,000 - 300,000 light years (1 light year = 6 trillion
miles = 9.3 trillion kilometers)
and has a thickness of several thousands of light years. The
disk of the Milky Way is very thin.
The appearance of the Milky Way is quite striking (probably). In the
center of the disk is a bulge out of which extends
several spiral arms. The Solar System is located in one of the
arms roughly two-thirds of the way out from the center of the disk.
The Solar System orbits the center of our Galaxy with a speed of roughly
220 kilometers per second or 800,000 kilometers per hour!
Can you estimate the mass of our Galaxy?
Comment -- The Milky Way galaxy has another componet (in addition
to the visible disk). There is a large spherical component to the
Milky Way which is made up of nonluminous material ( Dark Matter).
The Milky Way is dominated by this Dark Matter component. Perhaps
90 % of the Milky Way is nonluminous. This is also true for the
Universe where as much as 99 % of the Universe may be nonluminous!!
The average mass of a star in the Milky Way galaxy is 0.3
M . The Sun is
slightly larger than average, but it is not
really that far out of line. It seems to be just 1 out of the hundred
billion stars which make up the Galaxy. It is not atypical. Given
such facts, it is not unreasonable to suspect that the Solar System is
not unique. We will return to this issue at various times in the future.
. The Sun is
slightly larger than average, but it is not
really that far out of line. It seems to be just 1 out of the hundred
billion stars which make up the Galaxy. It is not atypical. Given
such facts, it is not unreasonable to suspect that the Solar System is
not unique. We will return to this issue at various times in the future.
The Solar System displays a
seemingly incomprehensible amount of diversity.
However, on a closer look,
we see many regularities and patterns in the Solar
System. It is these regularities and patterns which hold the key to our
understanding of the mechanics of the formation of the Solar System.
DYNAMICAL REGULARITIES
I have already mentioned, at one time
or another, all of the dynamical regularities
of the Solar System. The principal ones are:
- All planetary orbits are roughly in the same plane -- low inclinations
- All planetary orbits are roughly circular -- small eccentricities
- All planetary orbits are in the same sense -- CCW as viewed from the North
Some secondary regularities are:
- Most planets rotate in the same sense as they orbit
- The rotation axes of most planets are roughly
perpendicular to the eliptic
The above general properties of the motions of the planets are
quite significant.
There are also some vexing properties which people also need to explain, e.g.,
- The Sun contains over 99 % of the mass of the Solar System, but contains
less than
1 % of the angular momentum (why does the Sun rotate so slowly?)
DYNAMICAL REGULARITIES
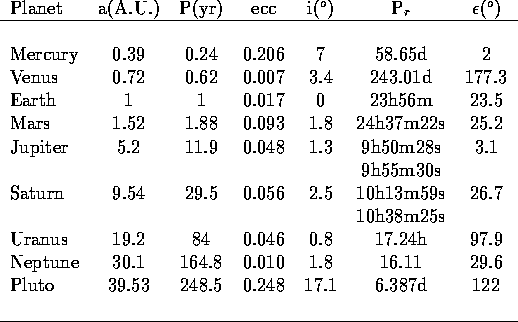
Any successful theory for the origin of the Solar System must
explain these facts.
PLANETARY REGULARITIES
The planets also show distinct regularities in that they
can be divided up into three distinct classes: Terrestrials,
Jovians, and Icy planets. In tabular form, we have
Planetary Properties. I

For a little bit of scale:
Mass of the Earth = 5.9742x10**24 kilograms
Mass of the Sun = 1.99x10**30 kilograms = 328,900 M
Diameter of the Earth = 12,756 kilometers
Diameter of the Sun = 1,392,000 kilometers = 109 D
So, adding up the masses of the planets (and including the asteroids
which are < 0.001 M ), we see that the Sun is > 99 % of the
mass of the Solar System.
), we see that the Sun is > 99 % of the
mass of the Solar System.
Random Comments
- the Jovian planets have extensive satellite systems
- the Jovian planets have ring systems
- ...
The regularities of the planets are clearly tied to how far they are
away from the Sun. The Terrestrial planets are closer to the Sun
than are the Jovian planets. In general, the Terrestrial planets are
smaller and more dense than the Jovian planets. Let's concentrate on
the density for a second (as this is an important point).
What do the observed properties of the planets imply?
Density
Planetary Properties. II
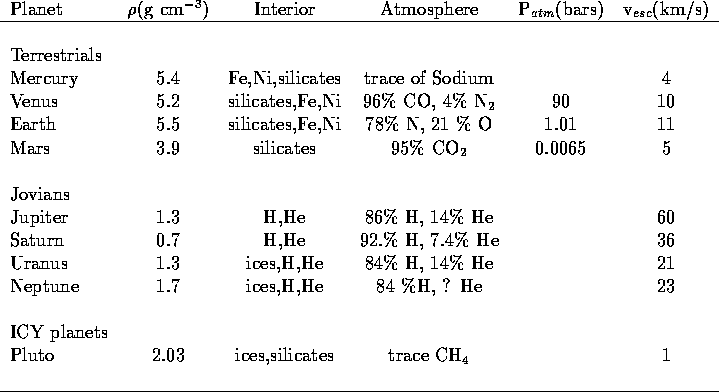
There is a clear distinction between the Terrestrials,
Jovians,
and Icy Planets in terms of their
- distances from the Sun
- masses and radii
- interior compositions (densities)
Comments--
Jim Imamura
Fri Oct 20 18:56:46 PDT 1995
 . The
visible material of the Milky Way is
contained in a thin rotating disk. The diameter of the disk is on
the order 100,000 - 300,000 light years (1 light year = 6 trillion
miles = 9.3 trillion kilometers)
and has a thickness of several thousands of light years. The
disk of the Milky Way is very thin.
. The
visible material of the Milky Way is
contained in a thin rotating disk. The diameter of the disk is on
the order 100,000 - 300,000 light years (1 light year = 6 trillion
miles = 9.3 trillion kilometers)
and has a thickness of several thousands of light years. The
disk of the Milky Way is very thin.
 . The Sun is
slightly larger than average, but it is not
really that far out of line. It seems to be just 1 out of the hundred
billion stars which make up the Galaxy. It is not atypical. Given
such facts, it is not unreasonable to suspect that the Solar System is
not unique. We will return to this issue at various times in the future.
. The Sun is
slightly larger than average, but it is not
really that far out of line. It seems to be just 1 out of the hundred
billion stars which make up the Galaxy. It is not atypical. Given
such facts, it is not unreasonable to suspect that the Solar System is
not unique. We will return to this issue at various times in the future.




 ), we see that the Sun is > 99 % of the
mass of the Solar System.
), we see that the Sun is > 99 % of the
mass of the Solar System.
