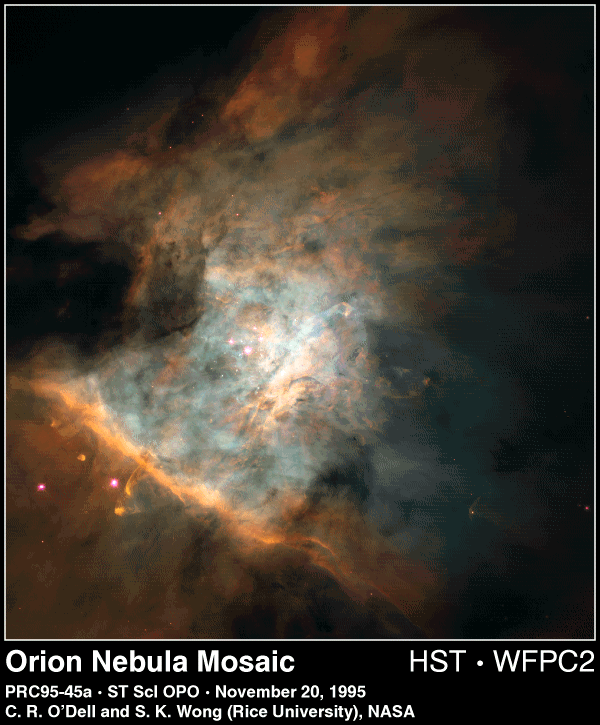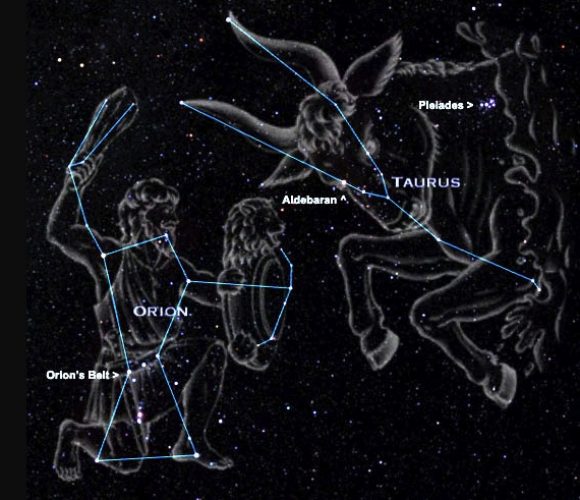
Orion battling Taurus |
Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs)
are huge, rarefied, cold gas clouds in the Interstellar Medium (ISM)
composed primarily of molecular hydrogen, H2,
helium with a sprinkling of everything else.
GMCs have huge masses, 10,000 to 10,000,000
Solar masses
GMCs have large sizes, tens of light years across
GMCs are dense, 100 to several million molecules atoms per cubic
centimeter (cc). One cc is roughly the volume of a sugar cube.
For comparison, the density of air in this room is roughly
1018-1019 molecules per cc,
and the average density of particles in our Galaxy (outisde
of these dense clouds) is
around 1 atom per cc.
GMCs contain dust which are agglomerations of billions of atoms of
mainly heavy elements and so there are only tiny amounts of dust.
Dust, however, is an efficient absorber and scatterer of visible light
and prevents us from seeing inside GMCs in the optical.
The dust does not affect IR and
microwaves and so they offer the best views of the star formation
process. There is roughly 1 dust particle per cubic football field in a
GMC!
GMCs are very cold T ~ 10 to 20 Kelvin
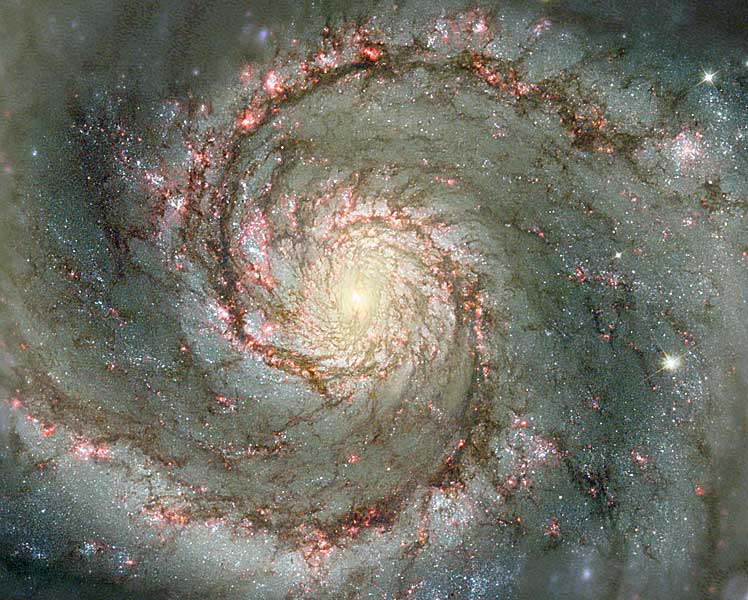
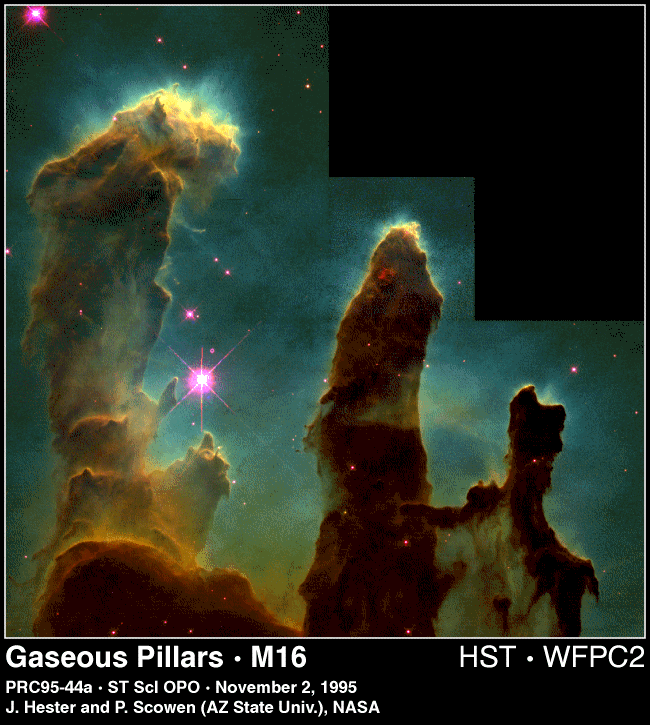
The most nearby example
of a GMC is in the constellation of Orion,
the Orion Giant Molecular Cloud, M42 complex (see panels).
|
The primary markers of star formation are
H II regions (gas clouds of ionized hydrogen),
O & B star associations and reflection nebulae,
and the Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) themselves.
(Also found near spiral arms are
H I clouds, neutral hydrogen gas clouds).
To get a handle on how these clouds fit together, I next
describe the material which resides between the stars of our
Galaxy, the material known as the
INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM, the ISM.
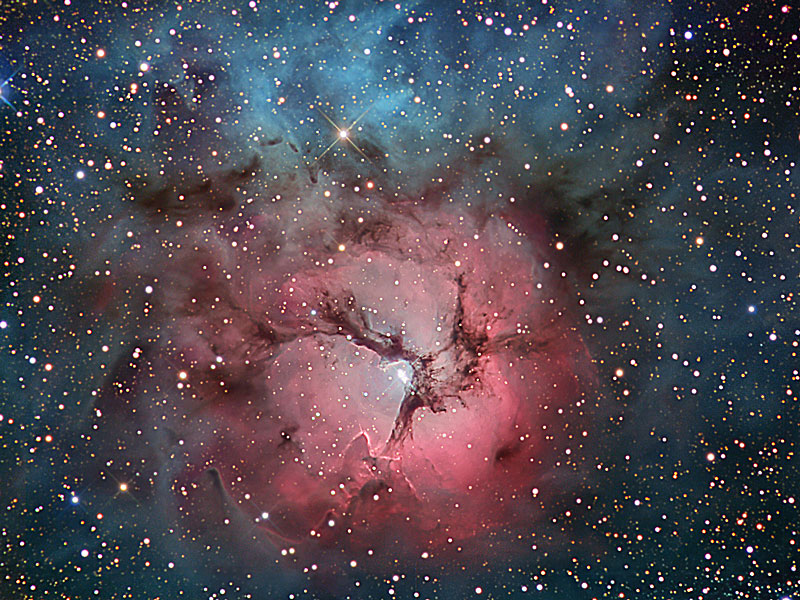

Trifid Nebula in Sagittarius, HII region |

Trapezium in Orion |
The Interstellar Medium (ISM)
The Milky Way
galaxy has a total mass > 100 billion Solar masses.
The material in-between the stars (the Interstellar Medium)
contains ten or so billion Solar masses -- the gas and dust are thus
about 10-15 % of the visible
mass of our Galaxy. This gas and dust are, however, quite
important as they are the material out of which stars form.
Make-Up of the ISM
- The ISM material is primarily gas:
- it is roughly
90 % hydrogen and 10 % helium, with just a touch of everything else.
- The
dust is very rare. Dust particles are
complexes of several billion atoms; they are usually
composed of carbon (graphite) and silicates.
This means that dust makes a very small contribution
to the mass of the ISM (< 1 %) and that it makes an even smaller
contribution to the number of particles in the ISM.
Structure of the ISM
The gas and dust are not spread uniformly throughout the Milky Way.
They are mostly confined to the disk of the Galaxy. Furthermore, they are
not spread uniformly throughout the disk. The ISM is lumpy. We have:
- Coronal gas -- dilute gas at temperatures of
around 3x105 K, which fills roughly 70 % of the volume of the
disk. The coronal gas has very low density -- around 0.01 % to 1 %
of the average
ISM density -- and so does not make a significant contribution
to the gas and dust mass of our Galaxy (~ 0.1 %). The coronal gas is
heated by supernova shocks.
- Neutral hydrogen Clouds (H I regions). The H I clouds have sizes
of ~15 light years, masses of ~ 100 M(sun), T ~ 50 - 100 K,
and densities of tens of millions of particles per cubic meter. They
make up roughly 40 % of the mass in the gas and dust but only a couple of
percent of the volume of the ISM. HI regions do not shine by starlight.
They produce something known as 21-centimeter Radiation:
radio emission from hydrogen which arises when the
electron flips its spin.
This is a critical technique for
seeing the ISM which is dominated
by neutral hydrogen, HI.
-
- GMC's are actually complexes of smaller clumps of material:
- small dense clumps
of material composed mainly of hydrogen molecules (H2)
with:
- T ~ 10-100 K
- densities of 100 million to
biilions of particles per
cubic meter
- sizes of 10s of light years
- masses of 104 to 107 M(sun) -- 105M(sun)
is typical
Although striking in appearance, GMCs fill only several hundredths of 1 percent
of the volume of the ISM.
Where the interstellar medium is cold and dense, molecules form (hence the
name GMC). Molecules play an important not only in the structure of the ISM
but also for the study of the ISM.
- Molecules may emit radio signals, the
wavelength of which indicates from which molecule it comes. For example,
- Hydroxyl OH
- Water H2O
- Ammonia NH3
-
Formaldehyde H2CO
- Carbon monoxide CO - useful for spiral arm study
- Molecular hydrogen H2
- Hydrogen isoCyanide HCN - see cloud around center of Milky Way
- Hydrogen is the overwhelmingly dominant component, but it is harder to
observe, and the other molecules are the observed tracers of the accumulation
- These radio signals, in addition to the IR that arises from the
dust, serve as sensitive probes of
star forming regions in GMCs.
- Ionized Hydrogen Clouds (HII regions).
(Eagle
nebula,
Eagle
nebula HST).
H II region mark sites of massive star
formation.
Massive stars (O & B stars) are very hot and so produce large
amounts of UV radiation. UV radiation is capable of ionizing hydrogen gas.
Lower mass stars are not hot enough to produce large amounts of UV and so
do not form large H II regions.
Associated with spiral arms and GMCs. These
are the red, glowing pictures that you see in the text. They glow red
because they radiate large amounts of hydrogen balmer alpha lines (which
fall in the red portion of the spectrum) which forms as the ionized hydrogen
gas (H II) recombines to form neutral atoms and radiates. H II regions
have temperatures on the order or 8,000-10,000 Kelvin with densities of
0.1 to 10,000 particles per cubic centimeter. They fill much less than 1 %
of the volume of the ISM.
- Reflection Nebulae (e.g.,
Pleiades), form around massive, hot stars.
One
sees the reflection of blue light by the dust particles in the cloud.
|
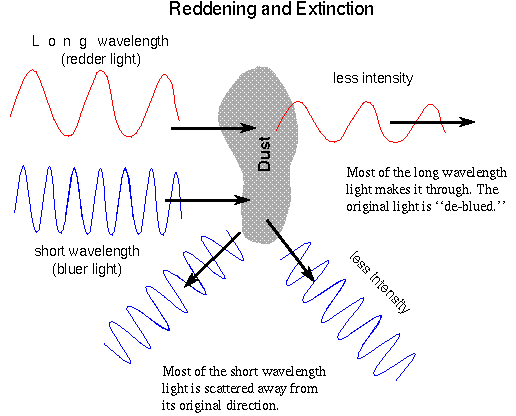 |
The dust scatters blue light toward us while the
red light streams straight through the dusty region.
- Dark clouds are regions of high dust concentration. The dust very
effectively blocks out the stars which sit behind them making what appears
to be a hole in the sky.
Ultraviolet radiation has helped in the study of the ISM allowing a
map of our local cosmic neighborhood to be formed.
Ultraviolet radiation can only be studied by instruments placed in orbit
above the Earth's atmosphere
The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) found a number of
regions of interstellar space that are much thinner (5000 atoms/m3)
and hotter (500,000 K) than expected
The Sun resides in the so-called
Local Bubble, a region
- about 100 pc across, containing about 200,000 stars
- thought to have been carved out by multiple supernova explosions several hunderd thousand years ago
- Such supernovae would have been spectacular events in the sky
|