Burning Chain
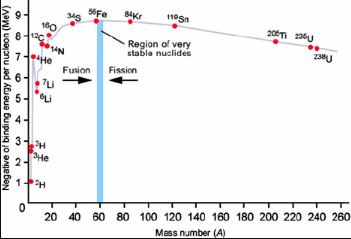
The nuclear fusion burning chains end with the production of iron. We can
understand as follows. The nucleus of an atom contains neutron (uncharged) and
protons (positive charges). The particles (known as baryons) are bound together
by the strong force. However, the electrical force
between the like-charged protons wants to disrupt the nucleus. The way the nucleus
gets around this is to insert neutral neutrons between the protons (to separate
them). We can actually make several isotopes of helium, 2 protons (di-proton),
2 protons + 1 neutron (He3), and the most common form 2 protons +
2 neutrons (He4).
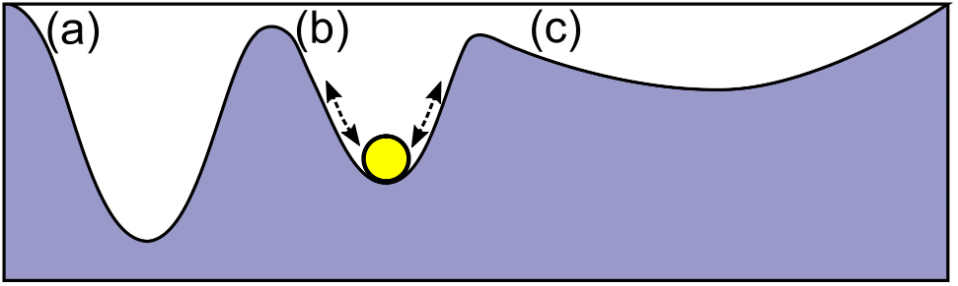
Based on the details of the structure of nuclei, nuclei range from
strongly bound to weakly bound (a to c) to unbound.
As for atoms, if two nuclei fuse to make a new nucleus, they release an amount of
energy (convert mass to energy) determined by the depth of the well. What does
mean for nuclear reactions?
The nucleus (a) is the most tightly bound, nucleus (c) is the most weakly
bound.
- Imagine we start with weakly bound nuclei such as hydrogen and combine them to
make a more tightly helium. This means we move from right to left. As the nuclei
drop into well (a), they fall and so release energy.
- Imagine we start with tightly bound nuclei such as iron and combine them to
make heavier elements. This means we move from left to right. As the nuclei
move from well (a) into well (c), they mus be lifted and so require energy
to proceed!
Iron is the most tightly bound nucleus and so, beyond iron, nuclear fusion reactions
act to steal energy from the system. In the case of a star, this would mean that
nuclear fusion would act as an energy loss mechanism rather than an energy
production mevchanism:
 |
In each successive stage of nuclear burning, the
reactions involve the ash of the previous step (that is, it involves more
massive nuclei with higher charges than for the previous step). Consequently,
each step takes place at higher temperature which is why
the later stages of burning requires a more massive star. Also note that
the amount of fuel for each successive stage is smaller. The combination
of the preceding leads to the successively shorter and
shorter amounts of time required for each stage.
|