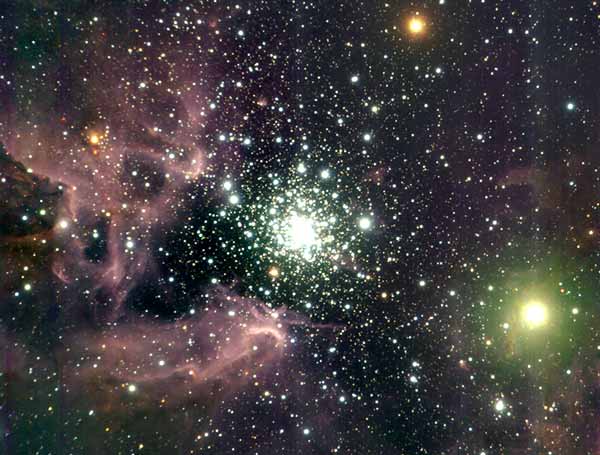

Open Cluster NGC 3603 |
Trumpler and Shapley |

Globular Cluster M15 |

Open Cluster NGC 3603 |
Trumpler and Shapley |

Globular Cluster M15 |
Herschel, and later Kapteyn counted stars in various directions to determine the shape of the Milky Way and our position in the Milky Way but came up with the wrong answer.
We are not at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Herschel and Kapteyn were unaware of the existence of dust in the interstellar medium (ISM).
Dust particles are agglomerations of billions of atoms. They are thought to be either silicate material or graphite material sometimes with a coating or water ice. Because they are composed of the trace elements of the Universe, they are exceedingly rare compared to hydrogen and helium in the interstellar medium. There is roughly 1 hydrogen atom per sugar cube (per cubic centimeter) in the ISM while there is roughly 1 dust particle (grain) per cubic footbal field in the ISM. They are, however, the principal absorbers and scatterers of radiation in the interstellar medium. Hydrogen atoms can only absorb very specific energies of radiation. They are transparent to the bulk of the radiation produced by stars and so they do not dim distant stars very much. Dust absorbs radiation over large wavelength regions very efficiently.
Dust only lets us see out to a few kiloparsecs (less than 5 - 10,000 light years into the Milky Way galaxy in optical light -- 1 parsec = 3.26 light years). This means that

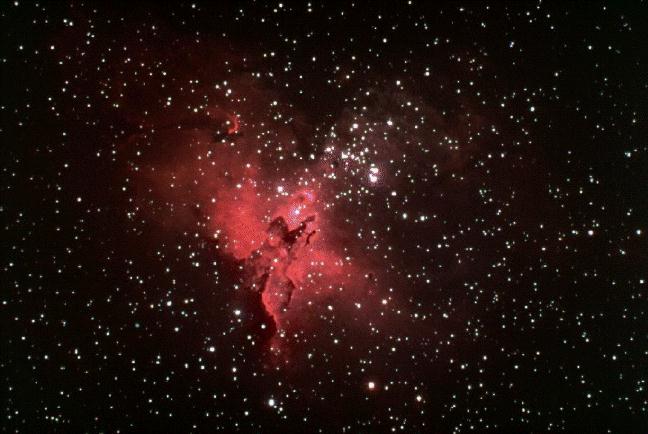
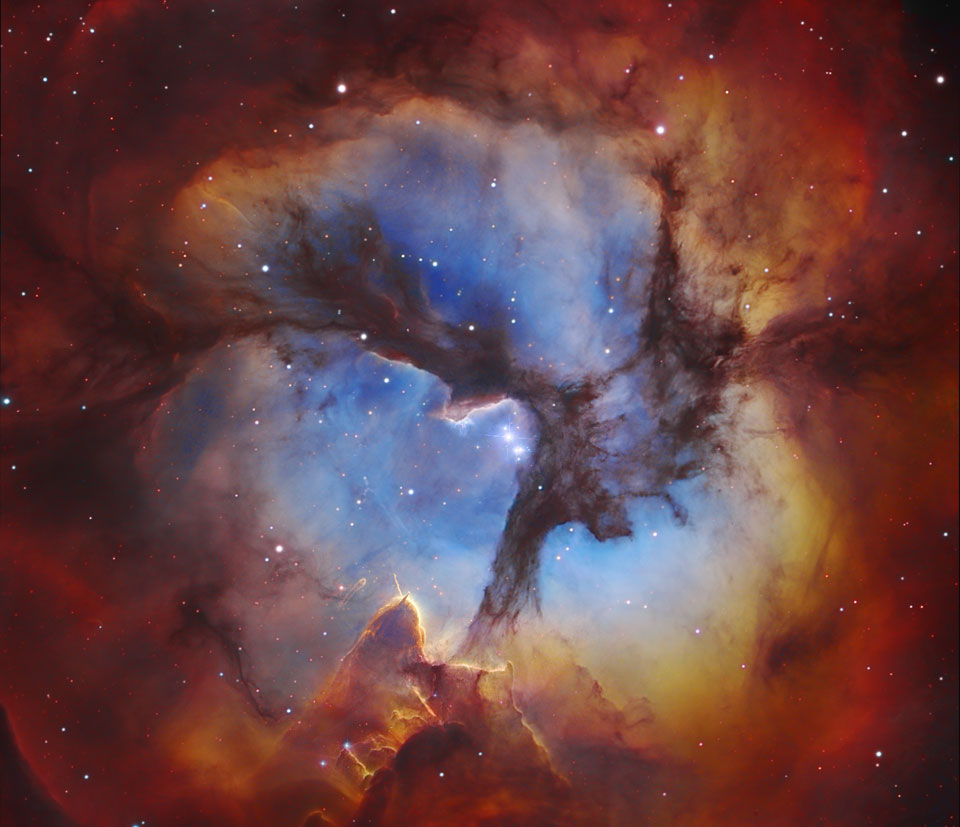
Below left we show a picture of the disk of the Milky Way in optical light. Note the dark bands which run through the Milky Way and the dark blemishes embedded in the disk. These arise because of obscuration of distant stars by dust. The picture on the below middle shows the Eagle Nebula, an interstellar gas cloud known as an HII region (region of ionized hydrogen gas). The dark bands in the Eagle Nebula are caused by obscuration from dust. The picture to the bottom right shows the Trifid Nebula a star forming region in the Orion Giant Molecular Cloud. The dark bands in the Trifid are caused by obscuration from dust as well.
 |
 |
 |
Below is a picture of the disk of the Milky Way galaxy taken in infrared light. At these wavelngths dust does not obscure objects, rather it radiates light (infrared, IR, light). This is understood because dust absorbs and scatters optical (visible light), the electromagnetic radiation to which our eyes are sensitive, and sheds this absorbed energy by re-radiating it in the IR portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

|
The existence of dust in the interstellar medium was inferred by Trumpler in the 1930s through studies of the star clusters known as Galactic Clusters. Without accounting for dust, Trumpler found that the sizes (in kilometers) of clusters increased with their distance from us. That is, the farther away a cluster was, the larger Trumpler inferred its true size to be! One would like to believe that clusters are more or less the same size and not that the clusters closer to us are systematically smaller than those farther away (shades of the Copernican Revolution).
 |
|
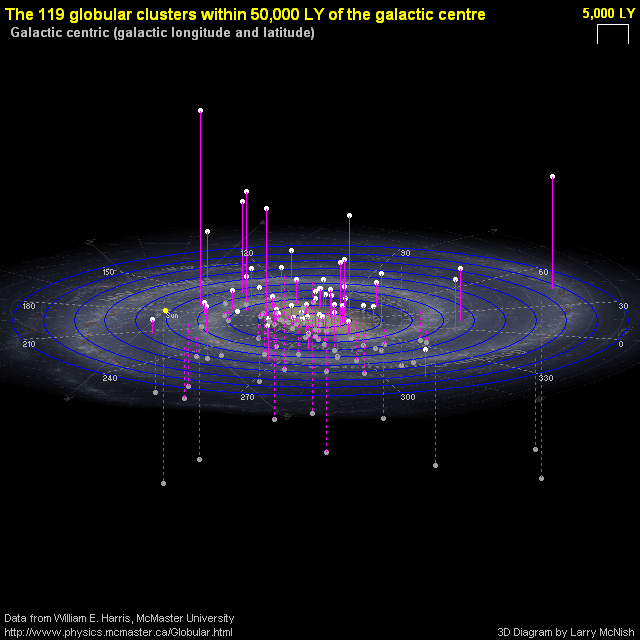 |
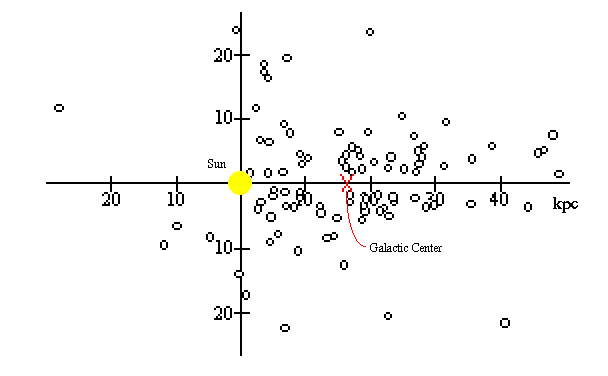
To the left is a figure that shows the 119 globular clusters in the Milky Way that are within 15,000 parsecs (~50,000 light years) within the center of the Milky Way Globular clusters are useful for this exercise because they exist above and below the disk of the Milky Way galaxy and so can be easily seen to large distances. Shapley observed these globular clusters in a method identical to that used by Herschel and Kapteyn when they counted stars. However, unlike Herschel and Kapteyn, Shapley was able to determine the distance to the globular clusters and not simply assume that they all had the same luminosity.
|
 |
Comment--Variable stars will be an important topic later as they serve as among the most reliable of distance indicators. The most important class of variable stars are the Cepheid variables which are evolved stars which are undergoing pulsations and periodically varying in luminosity. The key observational fact about them is that their intrinsic average luminosities are related to their pulsation periods For example, see Cepheid variables in M100.