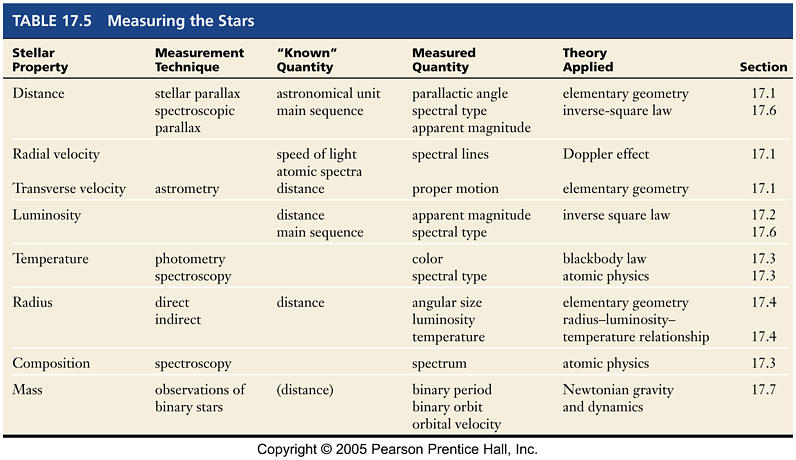
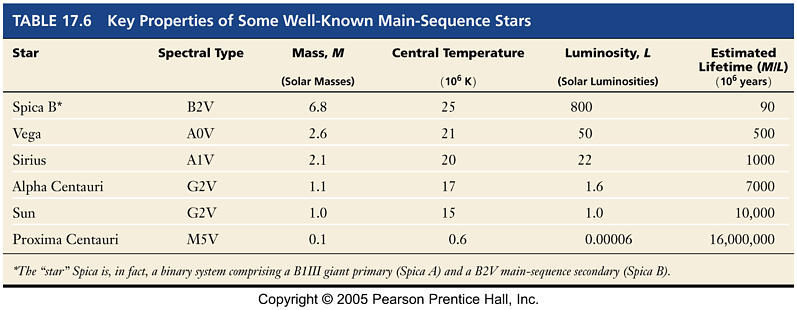
The Distances to the Stars
| 
|
| Measuring the Stars |
|---|
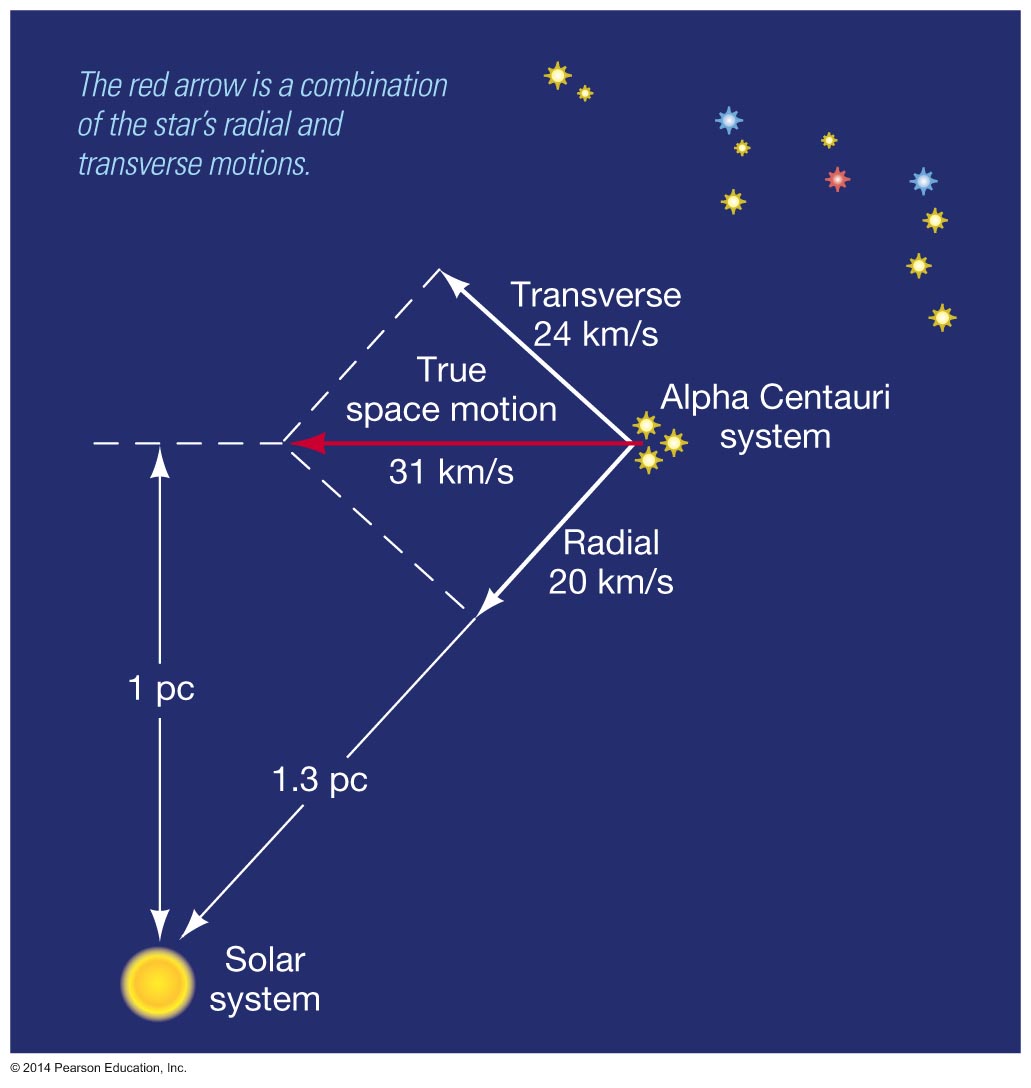
| Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main Sequence |
| 
|
| 
|
|
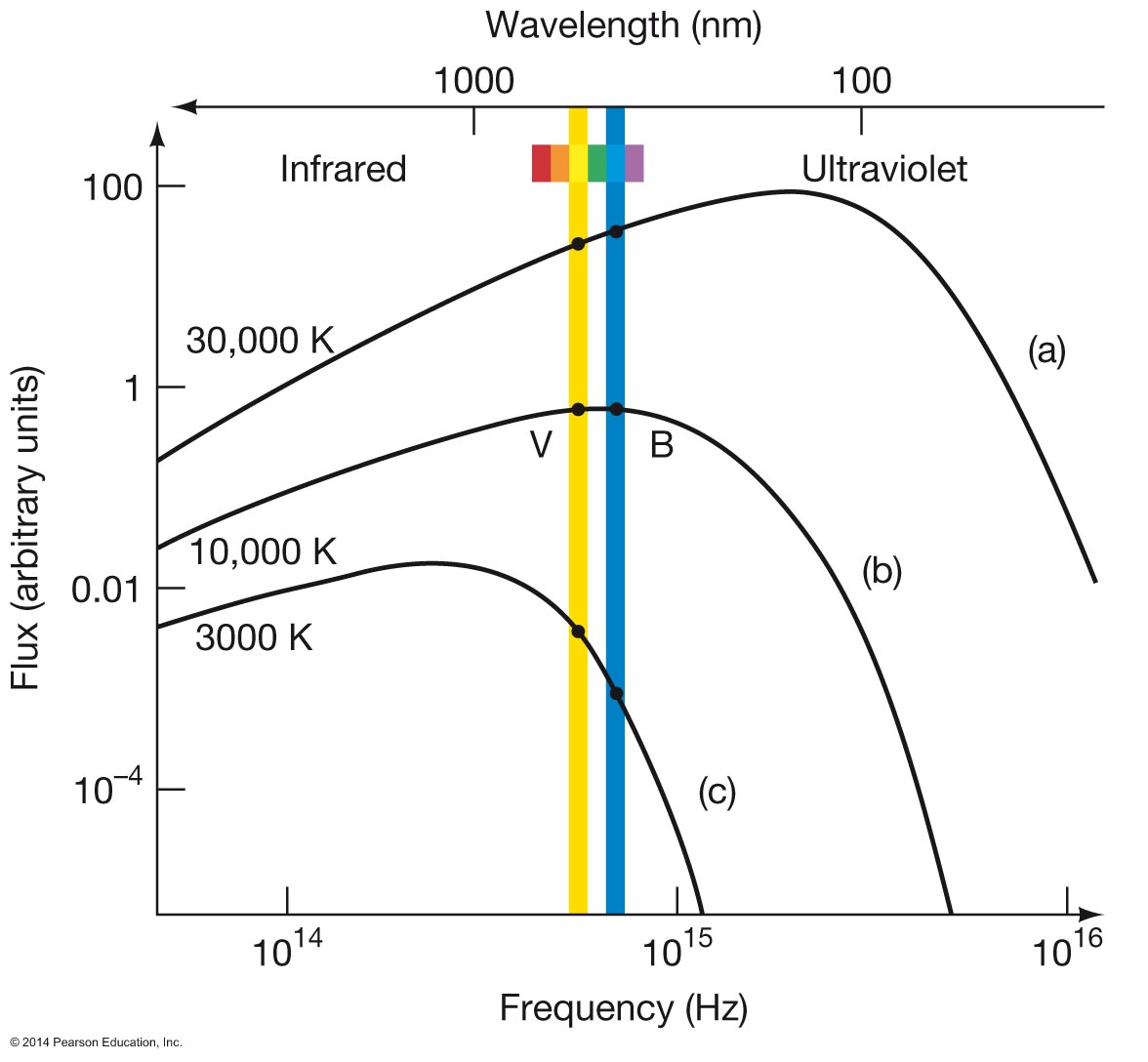
Area x T4, not just T4
represents an increased area, or a radius increase of 1,000 that is, type O has a radius 1000 times the radius of type M The above equation can be rearranged to derive an equation for the radius: or
| 
|
|
as shown in the textbookSirius has absolute magnitude 1.45 So |
Brightness | Apparent Magnitude |
Luminosity |
Absolute Magnitude |
| 
|
|
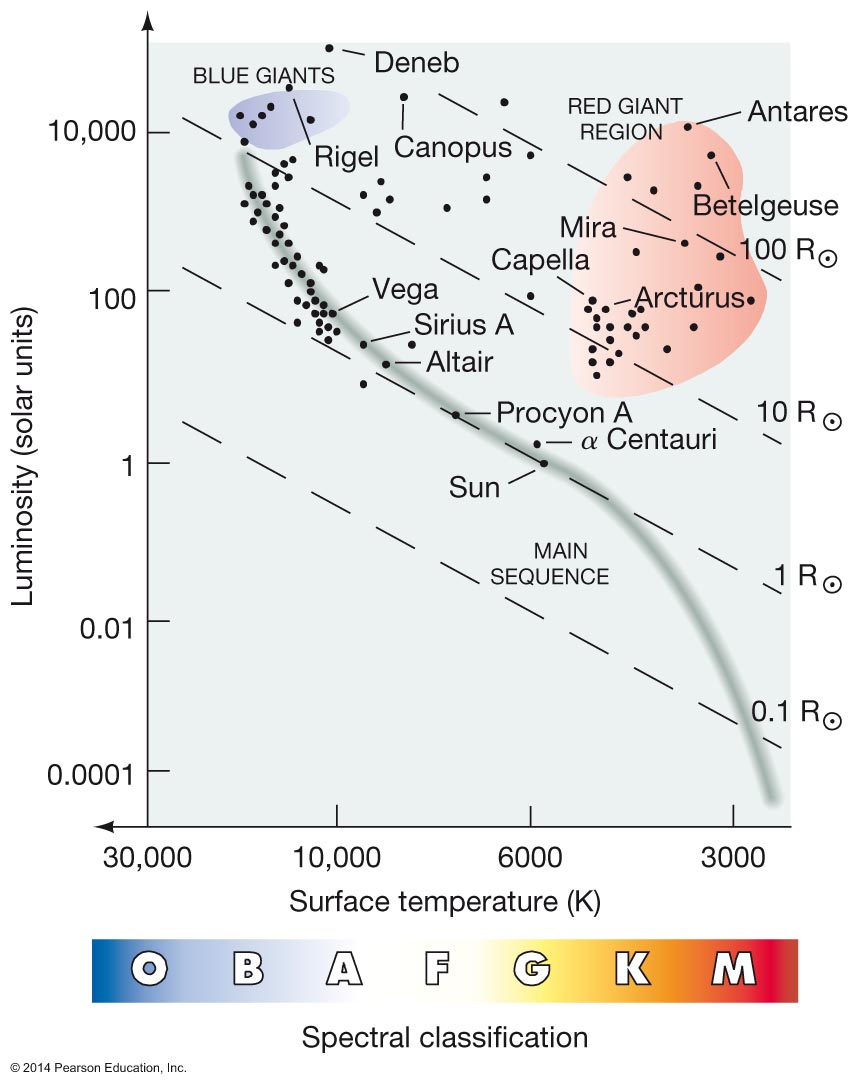
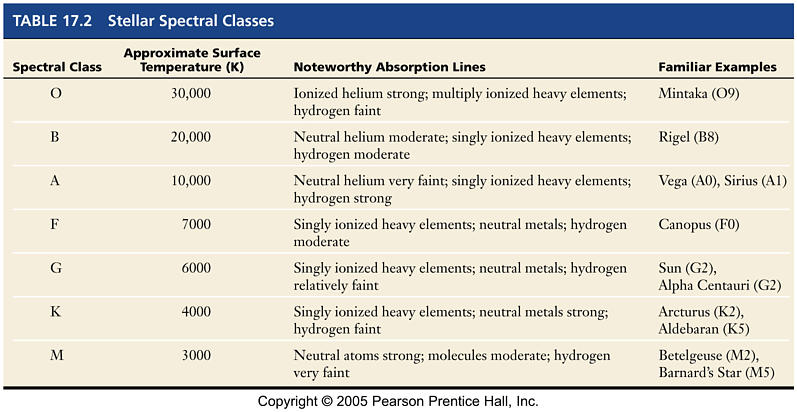
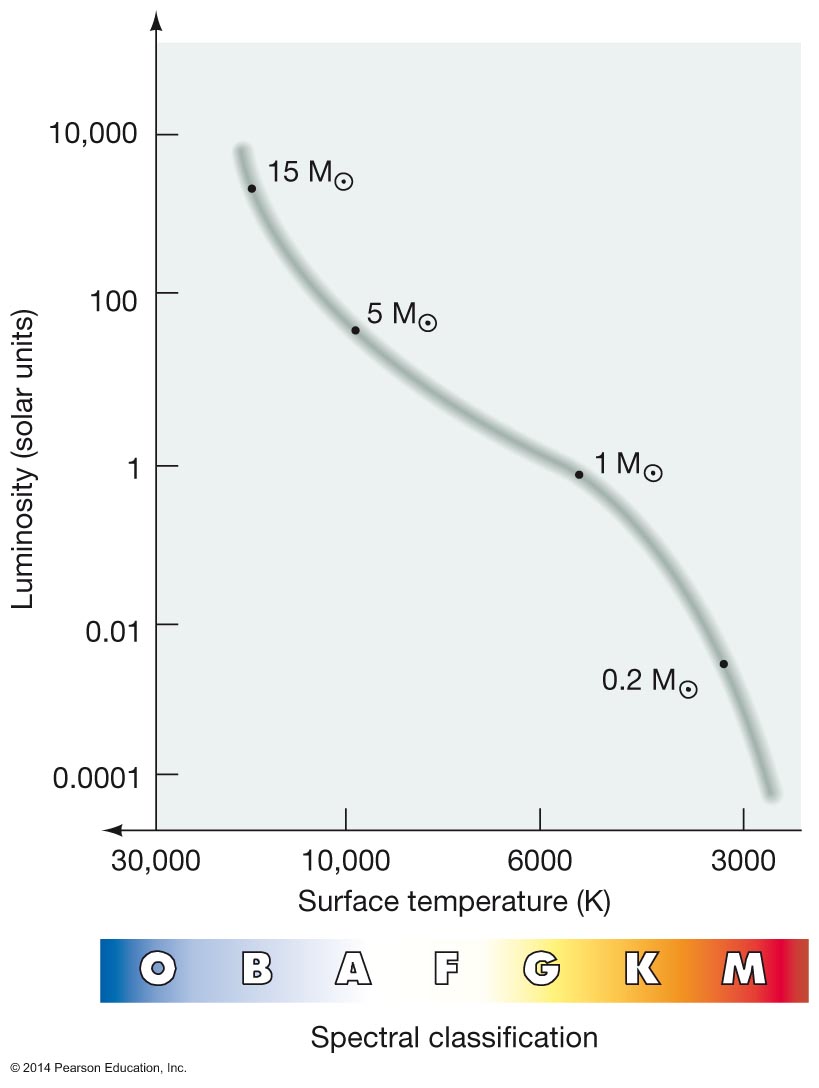
H-R Diagram is plot of Luminosity vs. Spectral Class Distribution of "Main Sequence" stars
Different classes of stars populate different regions of the H-R diagram
In our Solar neighborhood
|  
|
| 
|
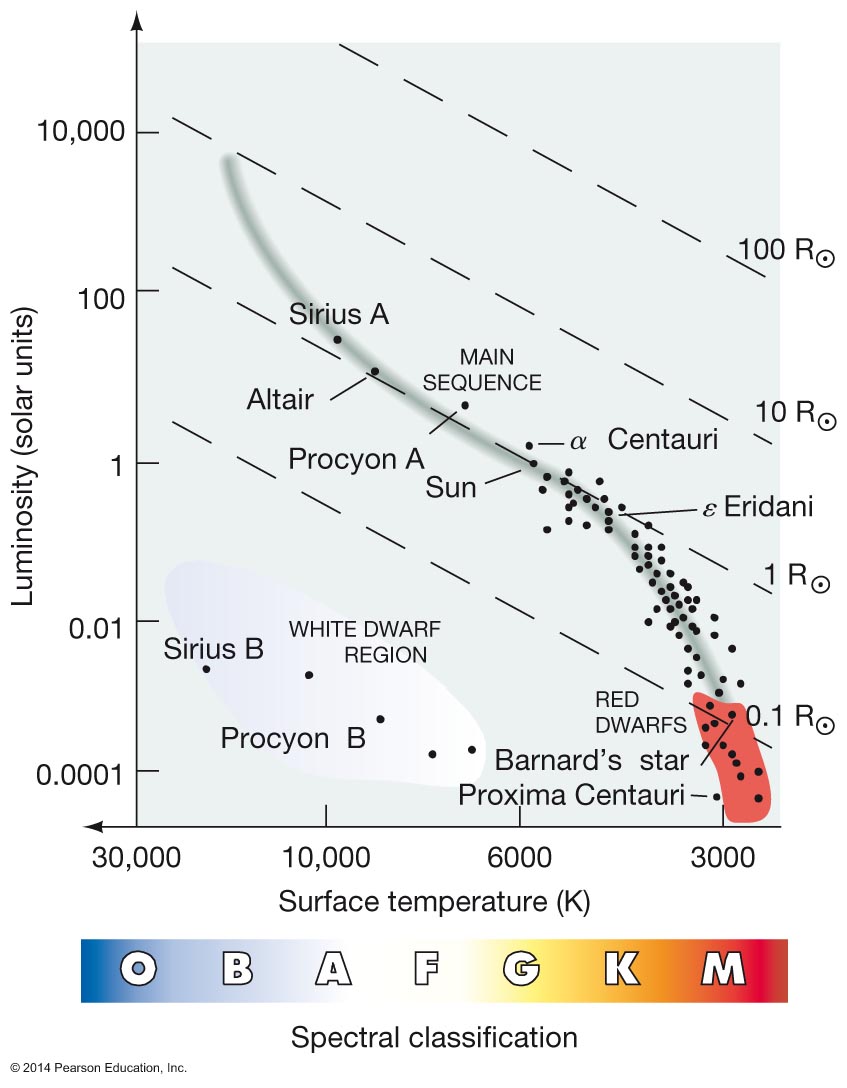
Only distances to stars on the main-sequence can be correctly determined by
the simple procedure outlined above under spectroscopic parallax
Can we distinguish stars that are off the main-sequence by their spectra?
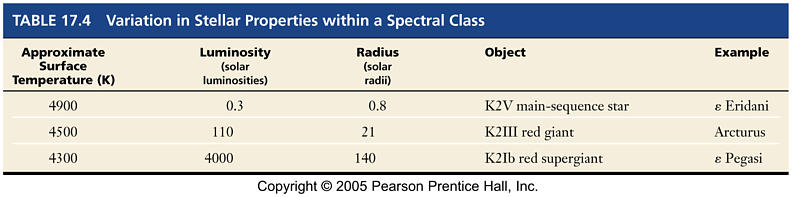
Technical Difference in Spectra of Same Spectral Class based on the width of lines width of lines determine luminosity classes Ia-V | 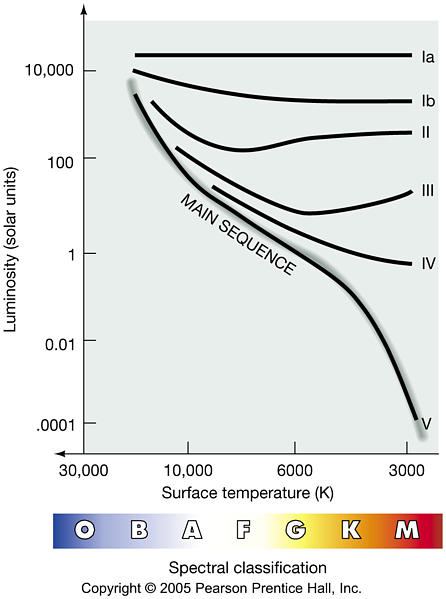
|
Example binary star: Sirius (the brightest star in the sky)
| 
|
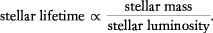
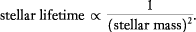
|  H-R Diagram for the Pleiades |
|  H-R Diagram for Omega Centauri |