Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
- First observer to use a telescope to view the sky.
- Discovered terrain on the Moon.
- Discovered sunspots and observed rotation of the Sun.
- Discovered four moons of Jupiter.
- Observed orbit of Venus around Sun, evident from phases and varied apparent size.
- Finally, Galileo concluded that the Copernican theory was supported by his observations and published a book with his conclusions.
- In 1600, the astronomer Giordano Bruno had been burned at the stake in Rome for such heretical teachings.
- Galileo was banned by the Roman Catholic Church from continuing his work, but he did continue until 1633 when he was threatened with severe punishment and put under house arrest.
- Galileo was imprisoned for the last decade of his life for his belief in the Copernican theory.
- In 1992, nearly four hundred years later, he was forgiven by the Church
| 
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
| |
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630)
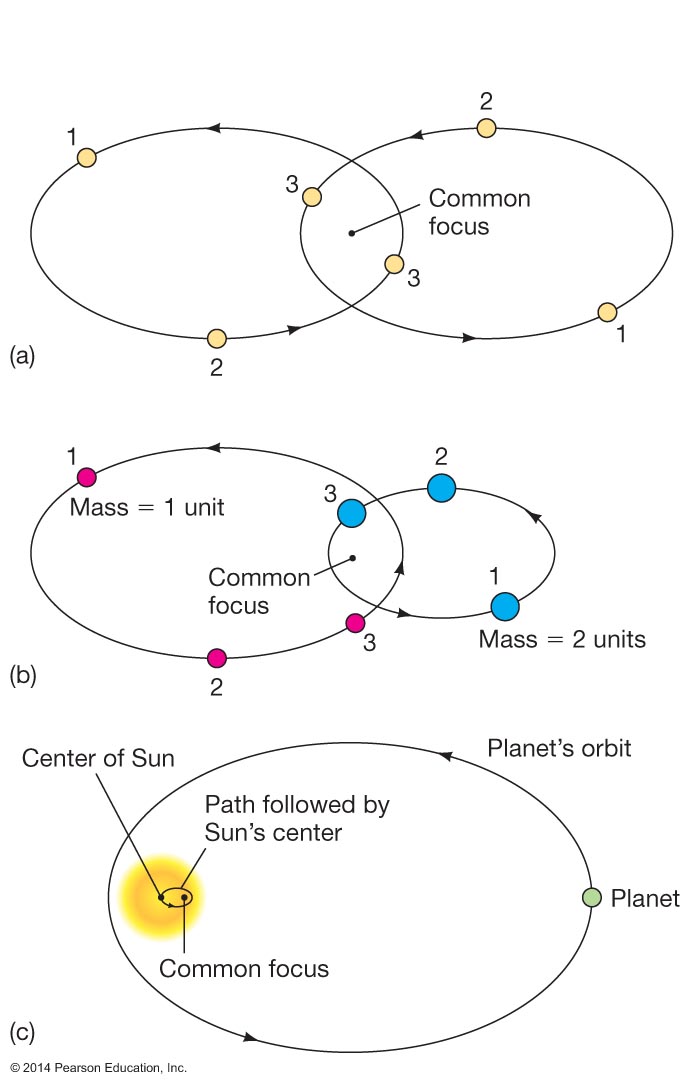
- Determined orbits of planets using measurements made from different times of the
year, meaning the Earth was at a different point in its orbit around the Sun (triangulation)
-
Kepler's laws of planetary motion
| 
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630)
- Issac Newton (1642-1727)
- While Kepler's laws were powerful in describing the orbits of the planets,
they were not understood from an underlying theory.
- Why does the Heliocentric model of the universe work?
- Why do the planets orbit the Sun?
- What prevents the planets from flying off into space?
- What prevents the planets from falling into the Sun?
- Why do the planets revolve around the Sun endlessly?
- Issac Newton developed the understanding of the way all objects move and interact.
- Newtonian mechanics - three basic laws of motion
| |
|







 ,
,