Interactive
Lecture Demonstrations
Prediction
Sheet--Newton's 3rd Law
Directions: Click here to download the Prediction Sheet on
which you will record your predictions. Write
your name at the top to record your presence and participation in these
demonstrations. For each
demonstration, write your prediction on this sheet before making any
observations. You may be asked to send this sheet to your instructor.
|
Demonstrations
1, 2, 3:
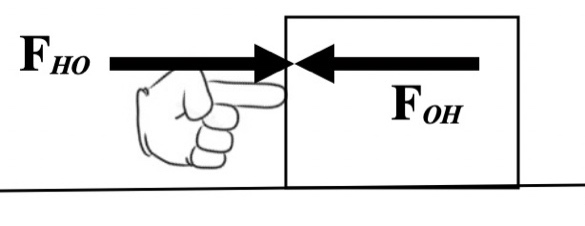
Someone pushes an object on a smooth surface. The block experiences a
constant frictional force opposite to its motion. Compare the following two forces in magnitude and direction, FHO
(the force of the Hand on the Object) and FOH (the
force of the Object on the Hand) during each of the three
demonstrations described below. Demonstration 1: The object is
being pushed at a constant velocity.
Predict how the force FHO compares FOH.
How does the magnitude of FHO compare to the force of
friction? What is the net force on the object? Demonstration
2:
The object is pushed so that it speeds
up. Predict how the force FHO compares to FOH.
How does the magnitude of FHO compare to the force
of friction? What is the net force on the object? Demonstration
3:
The block is pushed so that it slows
down. Predict how the force FHO compares to FOH.
How does the magnitude of FHO compare to the force
of friction? What is the net force on the object? Only after you have made all of your
predictions, click here to view a video of one
object being pushed by another. Force sensors measure the two forces. In each
case, observe the magnitudes of the two forces, and compare to your
predictions. Explain any differences. |
|
|
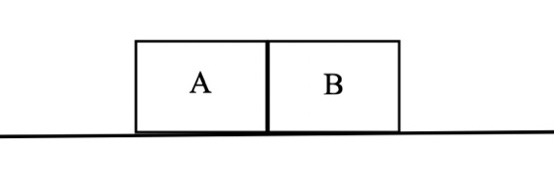
Demonstration 4: Two identical carts (called Car A and Car B)
are given pushes so that they move toward each other at the same speed. Predict how FAB (the
force of Car A on Car B) compares to FBA (the force
of Car B on Car A) during the collision.
How do the directions of the forces compare? Only after you have made your
predictions, click here to view a video of
the situation. Observe the two force and compare to. your predictions.
Explain and differences. |
|
|
Demonstration 5: A cart is given a push so that it moves
toward an identical cart that is at rest (called Car A and Car B). Predict
how FAB (the force of Car A on Car B) compares to FBA
(the force of Car B on Car A) during the collision. How do the directions of the forces
compare? Only after you have made your predictions,
click here to view a video of the
situation. Observe the two force and compare to. your predictions. Explain
and differences. |
|
|
Demonstration 6: A massive (heavy) cart (cart A--like a
truck) is given a push so that it moves toward a light cart (cart B--like a
small car) that is at rest. Predict how FAB (the
force of the heavy truck on the small car) compares to FBA
(the force of the small car on the heavy truck) during the collision. How do the directions of the forces
compare? Only after you have made your
predictions, click here to view a video of
the situation. Observe the two force and compare to. your predictions.
Explain and differences. |
|
|
Demonstration
7:
Two identical objects A and B (same mass) are sitting against each other on a
level surface. There is an explosive charge between them. The charge is set
off, and the two objects move apart. During the explosion, predict how the
force FAB exerted by object A on object B during the
explosion compares to the force FBA exerted by
object B on object A. Only after you have made your
predictions, click here to view a video
of the situation. Observe the two force and compare to. your predictions.
Explain and differences. |
|
|
Demonstration
8:
In Demonstration 7, suppose that object A is much more massive (heavier) than
object B. When the charge is set off, the two objects again move apart.
During the explosion, predict the force FAB exerted
by object A on object B to the force FBA exerted by
object B on object A. Only after you have made your
predictions, click here to view a
video of the situation. Observe the two force and compare to. your
predictions. Explain and differences. |
|