The first three concepts
- Temperature corresponds to average energy of the particles.
- The relation is E = k T.
- E is the typical energy of an electron, photon, ....
- T is the temperature.
- k is a constant.
- e.g. 3000 K corresponds to 0.3 eV. (This is the recombination
temperature).
- Equilibrium and temperature.
- Consider 1H + e <--> H atom + photon.
- At kT = 3 eV: all dissociated.
- At kT = 0.03 eV: all combined.
- In between: after awhile, it will reach an equilibrium concentration
of combined atoms.
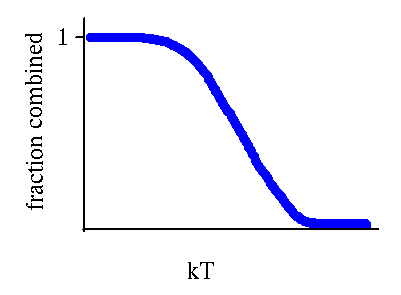
- Here is what might look like when half of the the atoms are dissociated.
- At any moment, some 1H + e <-- H atom + photon are happening.
If reaction rates aren't big enough, you can ``freeze out'' of
equilibrium.
- For example, after equilibrium, there were lots of photons left over.
- But the interaction of the photons with neutral atoms is slow, so the
photons just remained more or less forever.
- They are the same now, except for the cosmological redshift.
Davison E. Soper, Institute of Theoretical Science,
University of Oregon, Eugene OR 97403 USA
soper@bovine.uoregon.edu


