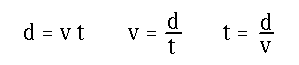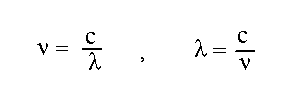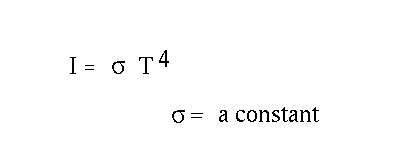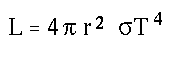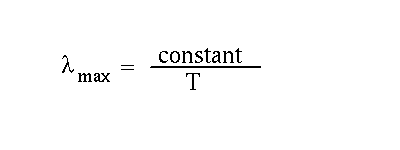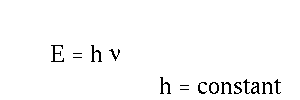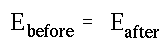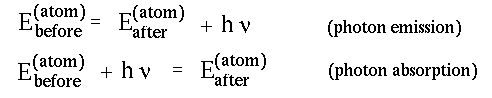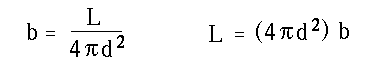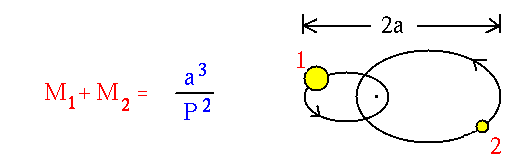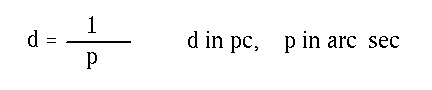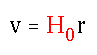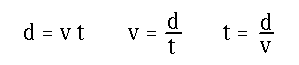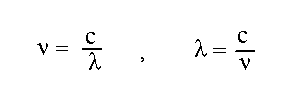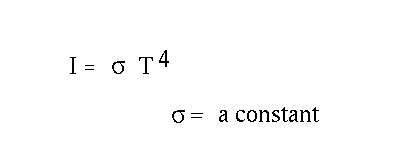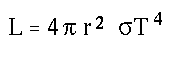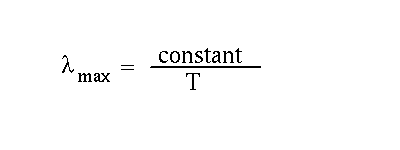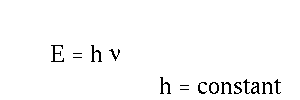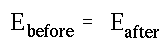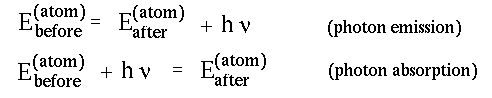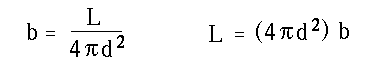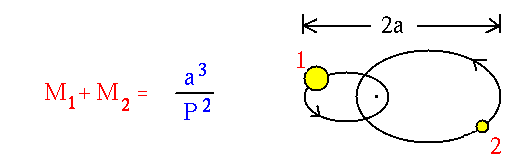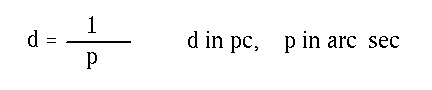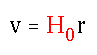Summary of physical laws for astronomy
Use of scientific notation.
Units of measurement.
Important numbers:
- Speed of light: 3 x 108 m/s.
- Astronomical unit: 150 x 106 km.
- Distance to center of the Galaxy: 25 kly.
- Distance to Andromeda Galaxy: 2 Mly.
- Age of the universe (from Hubble Law), roughly 10 x 109 y.
- Temperature of Sun at photosphere: 6000 K.
Laws:
- Distance d an object goes if it moves for time
t at speed v.
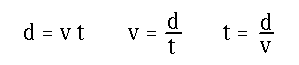
- Wavelength and frequency of light.
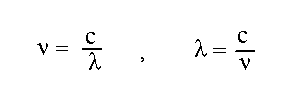
- Energy radiated by a blackbody per unit surface area per
unit time
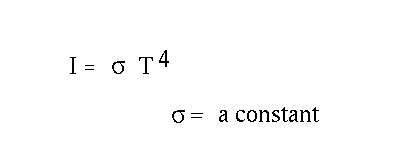
- Energy radiated by a whole star per unit time, given the radius
and surface temperature of the star.
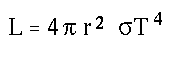
- Wavelength of peak intensity of blackbody radiation.
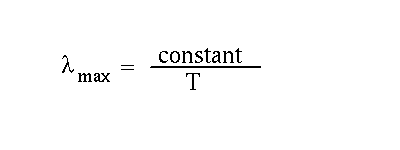
- Energy of a single photon
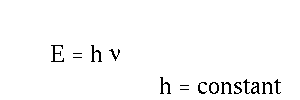
- Energy conservation
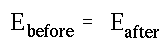
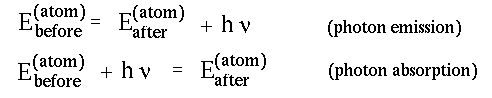
- Relation between luminosity of a star and its apparent brightness
when viewed at a distance d from the star.
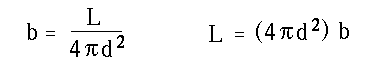
- Mass, gravity, and motion. The total mass of a two star system as
determined from the size of the star's orbits (the semimajor axis
a) in AU and the orbital period P in years.
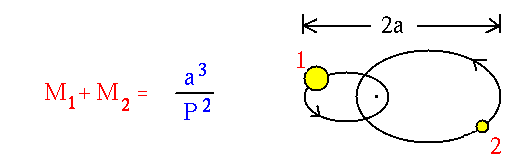
- Distance and parallax. The distance to a star in pc as determined
from its parallax angle in arc seconds.
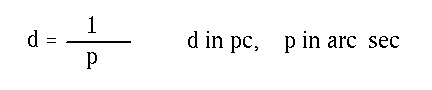
- The Hubble Law relating distance and speed of recession of distant galaxies.
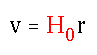
Davison E. Soper, Institute of Theoretical Science,
University of Oregon, Eugene OR 97403 USA
soper@bovine.uoregon.edu