Telescopes
and other devices for looking at the universe.
Reading: Chapter 6, Optics and Telescopes
What kind of electromagnetic radiation from space can we detect on Earth?
- radio and part of microwave: YES.
- microwave to infrared: NO, absorbed by atmosphere.
- visible plus part of infrared and part of ultraviolet: YES
- far ultraviolet: NO, absorbed by atmosphere.
- x-rays: NO, absorbed by atmosphere.
- gamma rays: NO, absorbed by atmosphere.
Before this century, astronomer could only observe in the optical
region. Then radio was added. Finally, with space satellites, we have
observations across the whole electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio & microwave
Use earth based detectors ("radio telescopes.")
In order to be able to point the telescope in a certain direction of
interest, it needs to be large. (For good pointing, need a size much
bigger than the wavelength of the radiation.) So people use a big dish
shaped object.

You are familiar with this because the same shaped objects are used
to pick up TV signals from satellites.
To get better angular resolution, you can connect several dishes with
electronic links. With suitable electronics, this gets the angular
resolution of one giant dish.
Optical
Use a telescope based on a mirror.
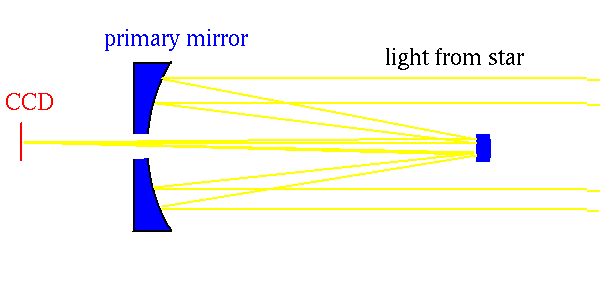
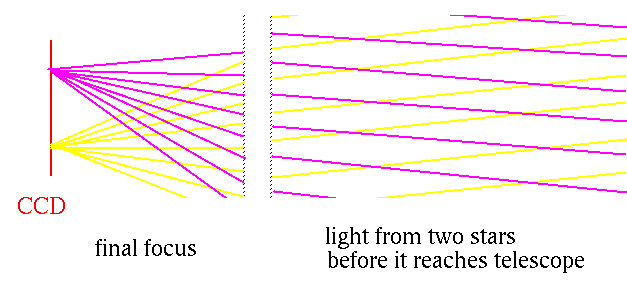
- a bigger mirror --> more light (see dim objects)
- a bigger mirror --> better angular resolution
- but only to a point.
- then turbulence in the atmosphere limits the resolution.
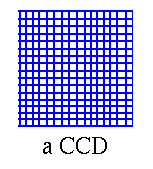
- to make best use of the available photons, use a charge
coupled device (CCD).
- this is an electronic gadget that turns photons into electric charge.
- it has lots of pixels.
- you send the record from each pixel to your computer.
Use a diffraction grating to divide the light from a star (or other object)
into its colors.
Space based observations.
- For many wavelenghts, need to get the detector above the atmosphere.
- Sometimes rockets or baloons are used, but satellites are best.
- There have been satellites for xrays, infrared, gamma rays, ...
- We will skip the study of how all of these work, but we will see
images from time to time in this course.
- Even for optical wavelenghts, getting above the atmosphere helps
with resolution. For this reason, we have the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Several Earth-based telescopes are bigger, but they are limited
by the atmosphere.
- In the first try, the Hubble mirror was messed up.
- Correcting optics were added by astronauts using the space shuttle.
- Now it is working fine.
Davison E. Soper, Institute of Theoretical Science,
University of Oregon, Eugene OR 97403 USA
soper@bovine.uoregon.edu




