ENERGY FUNDAMENTALS
Mechanics: Description of forces and
energies associated with moving objects; a manifestation of forces
acting on material objects
Components of Mechanics:
- Mass = measure of a resistance to force; the total number of
atoms in some material.
- Velocity = speed and directon of a moving object
- Acceleration = a change in the velocity of an object; an
object moving at constant velocity has no acceleration.
- Force = causes an acceleration; a change in velocity is a
manifestation of a force being applied to an object. If there are
no forces acting on an object there will be no acceleration.
Your intution already has physics
knowledge
A regular Physics course looks like this.
Our Version of Physics is more like the following:
1. You can't move a building
2. A train accelerates more slowly than a motorcycle
3. What goes up must come down
4. On the freeway you would rather have a headon collision with a
mosquito instead of a semi
5. You get tired after climbing a long flight of stairs
|
 Newton
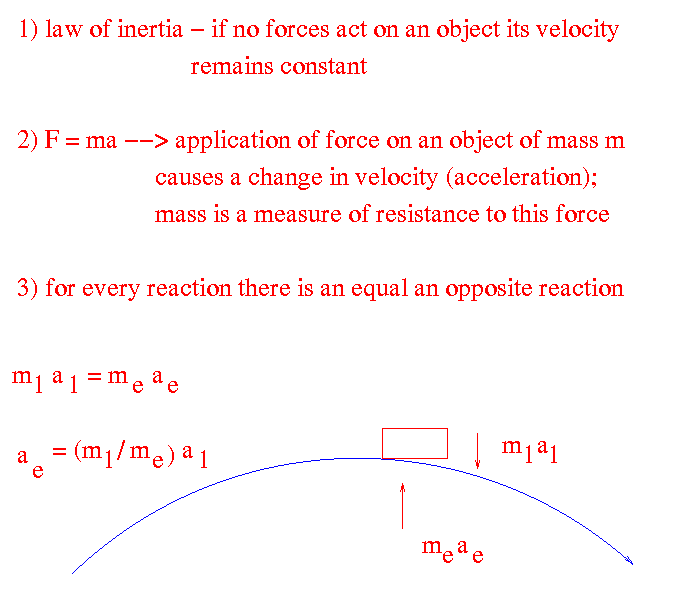
described mechanics fully in terms of three laws: constant
velocity with no forces, F= ma, equal and opposite reactions Newton
described mechanics fully in terms of three laws: constant
velocity with no forces, F= ma, equal and opposite reactions
|
Newton's Three Laws:
In Class Demos:
Newton's First Law
- Cart sitting on a track
- Air Puck
Newton's Second Law
- Fan Cart: Slow Fan Speed, Fast Fan Speed, Adding Mass to the
cart.
"Let the Force be with You..."
The fan attachment exerts an almost constant
force on the cart. What is the relationship between that
strength of that force and the cart's acceleration?
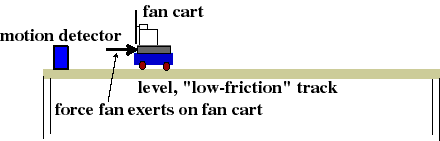
- What are the important and unimportant variables?
- Hypothesis I: acceleration is proportional to total
force (for constant mass).
- Experiment I: test hypothesis I. How do we do
this?
- What about when we vary mass?
- Hypothesis II: acceleration is inversely proportion
to mass (when force is held constant).
- Experiment II: test hypothesis II. How do we do
this?
- Result: Hypotheses I and II are correct. They can be
summarized as Newton's Second Law:
Definitions for speed, velocity, acceleration,
force and mass in words.
- Average speed of an object during a given time interval
is the change in its position divided by the length of that time
interval.
- Velocity is a measurement including both the
speed of and the change in direction of an object.
To completely specify an average velocity, one must
describe both its average speed and its average direction over a
given time interval. Average velocity is the change in
position-- including any changes in direction-- divided by the
change in time. --In the simple case of motion along a straight
line, average velocity would be the change in position divided by
the time interval--.
- Acceleration is a measurement of both the change
in speed and the change in direction of an object. Average
acceleration is the change in these two divided by the time
interval. --For the case of motion along a straight line, average
acceleration would be the change in velocity (which can be
negative or positive) divided by the time interval--.
- Experiments show that the acceleration of an object
is directly proportional to the net force acting on
it. This has several ramifications:
- As the net force applied on an object is increased, so is
the object's acceleration. If the acceleration of an object is
observed to decrease, then the net force acting on it must also
have decreased in magnitude.
- The direction of the acceleration is the same as the
direction of the net force.
- If no net force is exerted on an object, then its
acceleration is zero.
- Experiments also show that, for a given net force acting on an
object, the acceleration of the object is inversely
proportional to its mass.
- Thus, if the mass of an object is decreased, its
acceleration will increase.
- Mass in this context is sometimes called inertia--
its resistant to change in motion. An object with greater
inertia will resist change in motion (specifically, it will
accelerate less) than a less massive object, all other things
being equal.
- These two observations taken together can be summed up as
Newton's Second Law: The acceleration of an object is
proportional to the net force acting on it, and the constant of
proportionality is the object's mass.
What is Energy?
Introduction to Work and
Energy
One definition used by physicists to describe the energy of simple
objects is expressed in terms of work:
Energy is the capacity to do
work.
The more work done on a simple object, the more energy it has,
meaning that it has seen an increase in its capacity to do work. But
what, specifically, is work?
Scientists have a very particular definition for work-- a term
that can mean many different things in every day language (e.g., I
worked out, I got worked up or, we can work it out.). For simple
objects, work is defined as the net force exerted on the object times
the distance it is moved:
Work = Force x Displacement
Displacement is our word for moving some object some distance in
some direction. Displacement always has a direction associated with
it (I displaced myself 160km north up I5 and ended up in Portland).
Forces also have directions as well as magnitudes. It turns out that
the only important part of a force doing work is that part which
points in the direction of the displacement.
The terms Energy and Work are equivalent when applied top physics
principles.
Energy also comes in many forms, kinetic (something is moving),
potential (stored), heat (motion of molecules), etc. Energy is always
conserved. It is not created or destroyed but is just transformed
from one form to another.
In Class Demos:
- Cart and Scale
- Inclined Plane
- Pendulum and V Track
Power: Not to be Confused with
Energy
A measurement of energy delivered for a period
of time is called Power
Power = Energy/Time
Energy = Power * Time
Units are a good way to determine whether you are working with
power or energy. Let's break here and discuss units that are commonly
used in physics and in the study of Solar Energy Sytems. Click
here for notes on units
A kilowatt is a unit of Power
A kilowatt hour is a unit of Energy
Three Main Kinds of Energy
- Kinetic Energy
- Potential Energy
- Heat Energy ( The Kinetic Energy of microscopic
molecules)
Conversion of Energy:
Energy is not created or destoyed. It is converted from one form to
another.
Other Sources From the Net