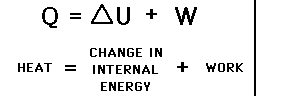
Laws of Thermodynamics
You can not subvert or change these laws:
The Zeroth Law (0): Systems are in equilibrium when they are at the same temperature.
0th Law: If A = B and B = C, then A = C
Thermal Equilibrium and Thermometers
If the objects are in Thermal Equilibrium NO Heat Energy will be transferred. If A is in thermal equilibrium with B and B is in thermal equilibrium with C the C will be in thermal equilibrium with A.
The First Law (1): Energy is Conserved in a closed system:
1st Law: Conservation of Energy:
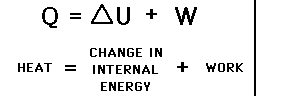
or Heat Flow(Q) = Change in Internal Energy (U)(Change in Temperature) + Work (W)(something moves such as a piston) Class Demo: The Special Syringe
|
Suppose I took a syringe full of air but with a little bit of paper at the bottom. Suppose I rapidly pushed down on the plunger? What would happen? How is this process represented by the first law of thermodynamics? What can we say about the internal energy of the air in the syringe? What can we say about heat energy transfer? |
|
2nd Law: Heat Flows from Hot to Cold
The Second Law (2) and The Law of Entropy:
Example: We can do this
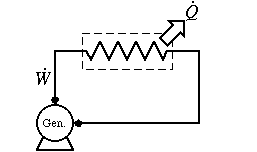
100% of electrical energy converted to heat by pushing a current
through a resistive stove element.
We can not reverse the process. The stove element will not heat up and directly produce electricity.
In the course of doing the original work we have increased the disorder to the system by heating it. In no way can we recover work of the disordered system without putting energy into the system.
To decrease local entropy requires work (energy).
is not and would require a lot of work to rearrange into the previous sentence
Temperature: Measurement of Internal Energy...how fast molecules are moving or vibrating in gas, liquids & solids. Commonly called Kinetic Theory.
Measure Temperature in degrees Celsius.
0oC ==> ICE
100oC ==> Boiling Water
23oC ==> Room Temperature (70oF)
Kelvin Scale based on Absolute 0.
Absolute 0 ==> Temperature where all molecular motion stops.
Lecture Demonstration on Temperature Scale: Extrapolating Absolute Zero
Absolute Temperature K, Kelvin Scale
0K = -273oC
0K = -460oF
273K = 0oC
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in degrees Celsius + 273