All roads lead to different places
Robert Lipshitz
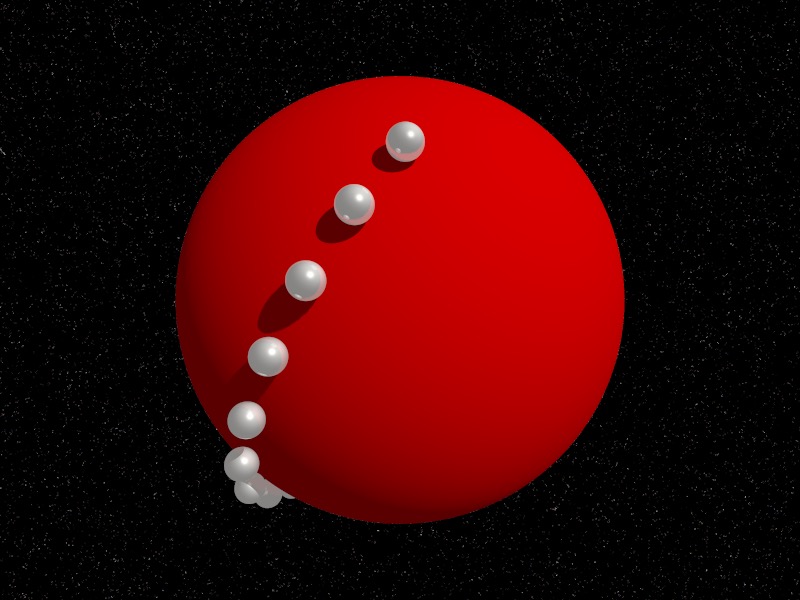
How do you study a space you cannot see? One way is through thought experiments: how would physics work on that space? On a sphere, there's no edge to roll off, but on a disk there is.
 |
 |
On a Möbius band, you'd have trouble telling up from down, or top from bottom.
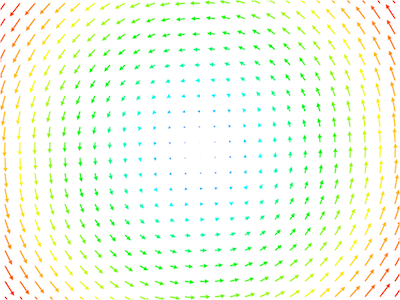
Fruitful thought experiments comes from thinking about how wind can blow on a space. On a sphere, like the surface of the earth, there is always somewhere that the wind is still.
Can you choose the wind -- a vector field -- so that, after some time, every point blows back to itself? What transformations can you get by following the wind for a shorter time?
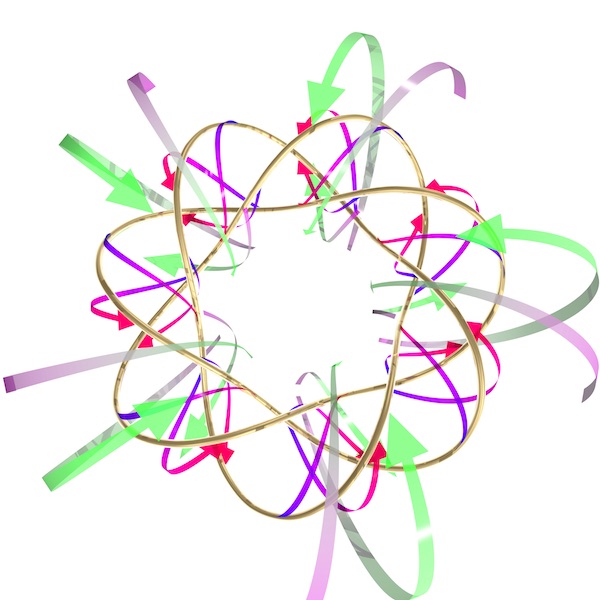
An eddy or whirlpool causes rotations. On a sphere, these are essentially the only kind of repeating, or periodic, transformations a wind can cause, and any rotation has one point that does not move. On a hypersphere, the analogue of a sphere but one dimension bigger, there is another kind of periodic transformation, where no point stays still. The arrows in ""All roads lead to different places" show one such transformation. The hypersphere is not drawn: it is the space the picture lies in, together with an imaginary point at infinity. Every point in space is the start of some arrow, and the end of another, though only a few of these arrows are drawn.
These arrows are described easily in terms of complex numbers: the
ones shown come from the formula where p=11 and q=6.
It was expected for more than a hundred years that essentially the only periodic motions of the hypersphere were rotations, reflections, and these free transformations (for various p and q). The hardest case to analyze turned out to be the free symmetries. It was finally proved in the early 2000s by the Russian mathematician Grigori Perelman. He was offered both a Fields Medal, the highest prize in mathematics, and the million-dollar Millenium Prize for his work, but declined them, writing that “I'm not interested in money or fame”.
The gold curve is a freely periodic knot: a closed loop which is taken to itself by one of these free, periodic transformations. Freely periodic knots are still an active area of study in pure mathematics. For example, can one always see a knot’s free periods in a simple diagram for the knot? It turns out that for so-called alternating knots the answer is yes; this was proved by Keegan Boyle in his University of Oregon Ph.D. and follow-up work in 2019.
On the surface of the earth, a sphere, there is always a Rome -- a place all roads start from or go to or wrap around. On a hypersphere, all roads can lead to different places.
The picture was made using POV-ray, an open-source ray tracer, which uses linear algebra to draw 3-dimensional scenes; and Sage, an open-source tool for mathematical computation.
References for further reading:
For the math-curious:
For math students or mathematicians:
- Charles Livingston, Knot Theory.
- Richard Hartley, "Knots with Free Periods".
- Keegan Boyle, "Odd Order Group Actions on Alternating Knots".