Astronomy 122
Mid-term Exam I Review
October 5, 2016
Astronomy 122
Prof. J. Brau
Exam will cover
Fundamentals
-
Scientific Notation
Know it.
- Scientific prefixes
- kilo (1000) like kilometer = 1000 meters
- Mega (106) like Megaparsec = 1,000,000 parsec
- milli (10-3) like millimeter = 0.001 meters
- micro (10-6) like micrometer = 0.000001 meters
- nano (10-9) like nanometer = 10-9 meters
- Distance Scale
- Light-year (9.46 x 1012 kilometers, or about 1013 kilometers)
- Parsec = 3.26 Light-years
-
Temperature Scales
-
Some Equations
The Stars and our Sun
The elements created in the Big Bang were mostly hydrogen and helium
- The Big Bang occurred about 14 billion (13.8 x 109) years ago
Stars are born within dark clouds in interstellar space
The Sun's source of energy is thermonuclear fusion, the fusion of
atomic nuclei with the associated release of energy
- This process of fusion creates the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen)
from the elements hydrogen and helium
The Sun is approximately 5 billion (5 x 109) years old, and it will continue generating
energy much as it is today for another 5 billion years
Nearby Stars
- Closest - Alpha Centauri System
- Three stars
- 4 light-years away
Brightest in Earth's sky - Sirius
Stellar deaths may be violent, such as the supernova explosion observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud
in 1987 (SN1987A)
The "star dust" that results from such explosions is the source of heavy elements, making possible the
existence of all things, planets, moons, animals, and plants.
Charting the Heavens and The Copernican Revolution
- Our Place in Space
- Galaxy clusters stretch over 1,000,000 light-years,
or about 1022 times the human scale.
- We inhabit no unique place in the universe
- Scientific Theory and the Scientific Method
- First documented use of scientific method dates to Greeks
- Scientific theory results from observation
leading to predictions, which can also be tested by observation
- must be testable
- must be simple
- should be elegant - tying together several phenomena
- The "Obvious" View
- The stars that make up a constellation are not actually close to one another in space.
- The Measurement of Distances
- Parallax is a method to measure relatively close distances in space.
- Other methods are used to build up a cosmic distance scale
- Ancient Astronomy
- The ancients studied changing nighttime sky for practical reasons
- navigation,
- tracking seasons for farming.
- The Heliocentric Model of the Solar System
-
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) revolutionized thinking about universe with heliocentric (Sun-centered) model in the 16th century.
- In fact, Aristarchus of Samos (310-230 B.C.) had proposed that planets revolve around the Sun, but this view did not catch on then.
- Galileo, Kepler, and Newton
- Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
- Took radical approach of actually performing experiments.
- First to use telescope to observe the sky.
- Among his discoveries was the evidence that the Sun was the center of the Solar System, supporting Copernican heliocentric model.
- Johannes Kepler (1571-1630)
- From measurements of the orbits of planets developed laws of planetary motion
- First law: the orbital paths of planets are elliptical (not circular), with the Sun at one focus.
- Second law: An imaginary line connecting the Sun to any planets sweeps out equal areas of the ellipse in equal intervals of time.
- Third law:The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis.
- Issac Newton (1642-1727)
- Developed three basic laws of motion and the Law of Universal Gravitation
- Newton's first law of motion: Every body continues in a state of rest or in a state of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by a force acting on it.
- Newton's second law of motion: When a force F acts on a body of mass m, it produces in it an acceleration a equal to the force divided by the mass.
Thus, a=F/m, or F=ma.
- Newton's third law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Newton's laws provide an excellent description of the motion of planets, stars, and galaxies
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation:
Every particle of matter
in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly
proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
- or
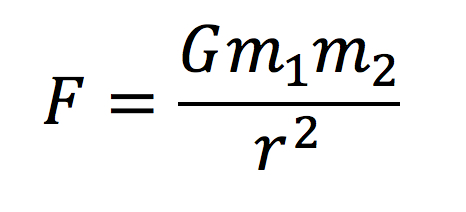 ,
,
where G is the gravitational constant (6.67 x 10-11 Newton/meter2/kilogram2)
Light and Electromagnetic Radiation
- Wavelength
-
Spectrum (long wavelength -> short)
............(low energy -> high energy)
- Radio(greater than 100 microns- or 100 x 10-6meters)
- Infrared(between 100 microns and 0.7 micron)
- Visible(between about 0.7 microns and 0.4 microns)
. . . (or between about 700 nanometers(nm) and about 400 nm)
- Ultraviolet(between about 400 nm and about 10 nm)
- X-ray(between about 10 nm and about 0.01 nm)
- Gamma-ray(below 0.01 nm)
- All electromagnetic radiation travels at the speed of light
. . . . . . . (300,000 kilometers/second)
- Radiation is composed of "photons" (packets of electromagnetic radiation)
- the "photons" behave as particles sometimes, and as waves at other times
- the "photons" have energies related to the "color" or wavelength
- short wavelengths -> higher energies
- long wavelengths -> lower energies
where E is energy (in Joules)
h is Planck's constant
(h = 6.63 x 10 -34Joule seconds)
and f is frequency in 1/sec, or Hz.
Photon energies are very small
For example, for visible light (0.5 μ m), f = 6 x 1014 /sec
|
wavelength x frequency = velocity = 300,000 km/sec |
|---|
So, E = 4 x 10-19 Joules
- "Windows" in the atmosphere
-
Generation of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic Radiation is generated by the movement of charged particles
- Electrons (negative charge) are most important
-
Blackbody Radiation
-
Peak wavelength decreases with temperature (Wien's Law)
- Total energy output increases with temperature
...........(increases as T4 - Stefan's Law)
- Surface temperature of the Sun is 6000 K
...........--> peak of spectrum in the visible light
-
Inverse Square Law
The apparent brightness of a star is inversely proportional to the
square
of its distance.
- Doppler Effect
- Wavelength of light from moving object is shifted
- Moving away ->
Red shift
- Moving toward ->
Blue shift
Spectroscopy
-
Absorption and Emission Lines
-
Kirchhoff's Laws
- Continuous spectrum
- Absorption-line spectrum
- Emission-line spectrum
-
Atoms and Molecules
- Photons
- The particle nature of electromagnetic radiation
- represents wave-particle duality
- photons can
be absorbed
or emitted by an atom,
boosting the electron to an excited
state (on absorption)
or bringing the electron to a lower energy state (on
emission)
- Since only certain energy states of the atom are allowed, only certain
wavelengths of photons are emitted or absorbed, explaining the spectral
lines.
-
Spectral Analysis
- Basic Optics
-
Refraction
- The bending of light as it crosses the boundary from one transparent material to another
- Red (long wavelength) bends less than blue (short wavelength)
Line Broadening
- Line broadening is caused by the environment in which the emission or absorption occurs
These lecture notes were developed for Astronomy 122 by Professor James Brau,
who holds the copyright. They are made available for personal use by students of the course and may not be distributed or reproduced for commercial purposes without my express written consent.
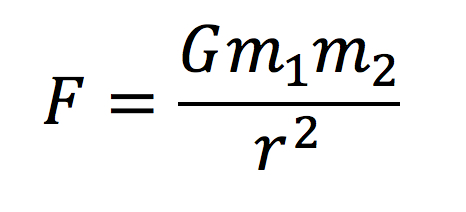 ,
,