Anion Sensing
Partner site with Johnson lab
Many anions are problematic environmental contaminants and are vital to many processes in nature, with anion binding proteins and transport
channels implicated in the mechanisms of many disease pathways. This avenue of research is a productive collaboration between the Haley lab
and that of UO colleague Darren Johnson to target new organic receptors
that selectively bind and sense anions. The project is a union of the synthetic expertise of the Haley group toward the assembly of
relatively rigid and inherently fluorescent molecules based on arylethynyl scaffolding with the extensive knowledge of the Johnson lab to
design and exhaustively analyze complex supramolecular systems.
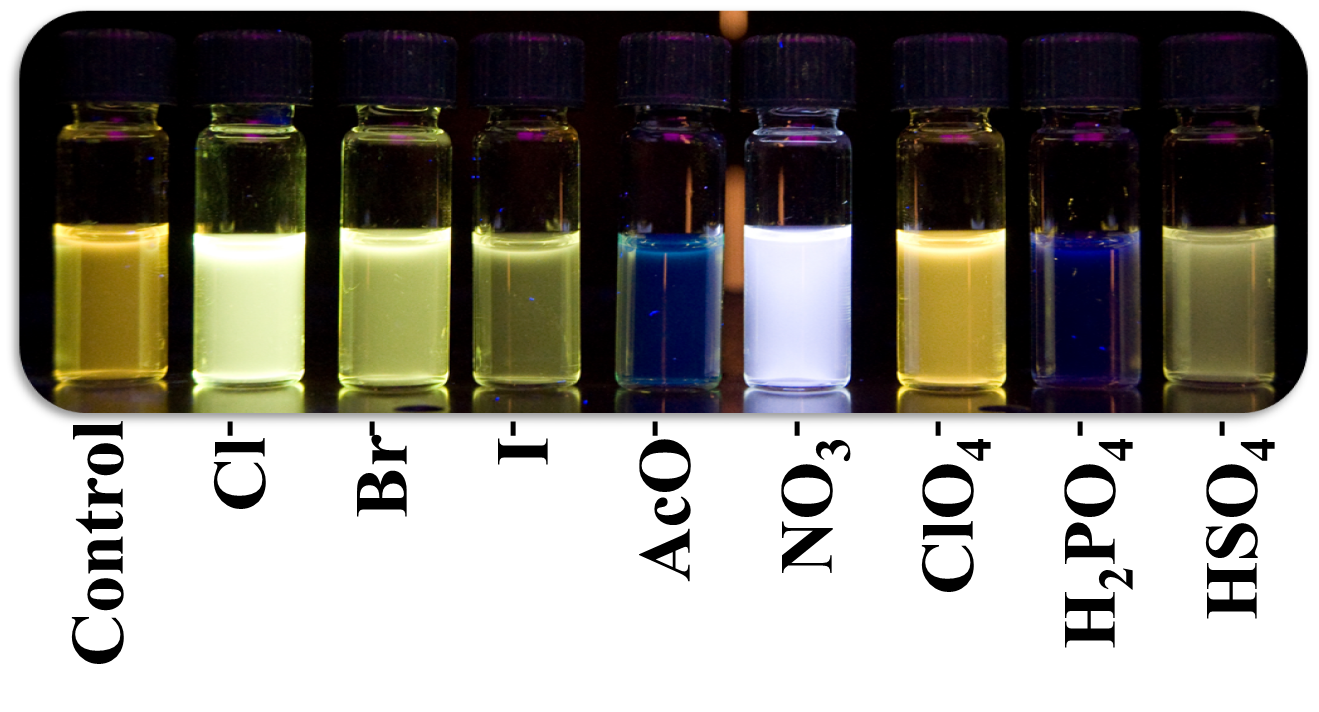
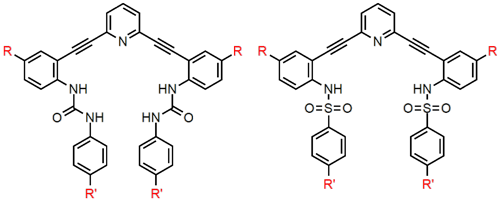

The modularity of our design strategy allows for exploration of a variety of recognition motifs for anions,
including electrostatic attractions, hydrogen bond interactions and attractions with electron-deficient arenes (anion-π, CH•••X–
hydrogen bonds and weak-sigma complexes). This flexibility affords the possibility of selectively binding anions that are challenging
to target with traditional approaches. Core and linker substitution provides another approach to tuning the selectivity of the
receptors by changing the shape and size of the binding pocket, in addition to modification of the fluorescent behavior through
adjustment of the electronics of the conjugated core fluorophore. The functionality of the receptors can also be adjusted to provide
water-solubility to the molecules or even cell membrane permeability. These sensors will have long-term applications in sensing,
imaging and/or remediating anions, which will impact public health in both discovering and removing environmental contaminants and
imaging the role anions play in biological processes.
Work on the bis(arylethynyl) bisurea based receptor class has also led to a successful start-up company,
SupraSensor Technologies. Co-founded by Haley, Johnson, and former graduate student Dr. Calden Carroll, SupraSensor targets nitrate detection for
applications in precision agriculture. Both the basic research from the Haley/Johnson collaboration as well as the applied science from Carroll and his
team were highlighted in an NSF-sponsored "Science Nation" video (http://www.nsf.gov/news/special_reports/science_nation/suprasensor.jsp).
Relevant Publications
Anion-directed self-assembly of a 2,6-bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine bis(amide) scaffold
Tresca, B. W.; Berryman, O. B.; Zakharov, L. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Supramol. Chem. 2016, 28, 37-44.
DOI:
10.1080/10610278.2015.1072199
Substituent Effects in CH Hydrogen Bond Interactions: Linear Free Energy Relationships and Influence of Anions
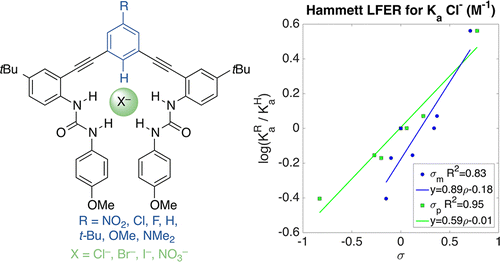
Tresca, B. W.; Hansen, R. J.; Chau, C. V.; Hay, B. P.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14959-14967.
DOI:
10.1021/jacs.5b08767
Facile Synthesis and Properties of 2-λ5-Phosphaquinolines and 2-λ5-Phosphaquinolinones
Vonnegut, C. L.; Shonkwiler, A. M.; Khalifa, M. K.; Zakharov, L. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13318-13322.
DOI:
10.1002/anie.201507696
‘Off-On’ Aggregation-Based Fluorescent Sensor for the Detection of Chloride in Water
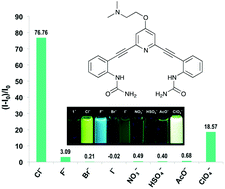
Watt, M. M.; Engle, J. M.; Fairley, K. C.; Robitshek, T. E.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 4266-4270.
DOI:
10.1039/C4OB02409E
Solid-State Examination of Conformationally Diverse Sulfonamide Receptors Based on Bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine, -Bipyridine, and -Thiophene
Berryman, O. B.; Johnson, C. A.; Vonnegut, C. L.; Fajardo, K. A.; Zakharov, L. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 1502-1511.
DOI:
10.1021/cg5018856
Ion and Molecular Recognition Using Aryl–Ethynyl Scaffolding
Vonnegut, C. L.; Tresca, B. W.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 522-535.
DOI:
10.1002/asia.201403212
Cover art:

Exploring anion-induced conformational flexibility and molecular switching in a series of heteroaryl-urea receptors
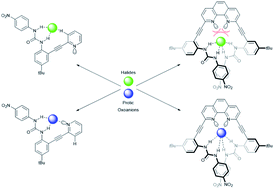
Gavette, J. V.; Evoniuk, C. J.; Zakharov, L. N.; Carnes, M. E.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2899–2905.
DOI:
10.1039/C4SC00950A
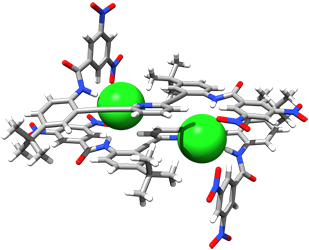
Intramolecular N–H•••Cl hydrogen bonds in the outer coordination sphere of a bipyridyl bisurea-based ligand stabilize a tetrahedral FeLCl2 complex
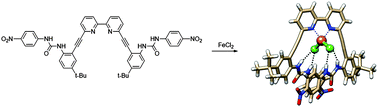
Gavette, J. V.; Klug, C. M.; Zakharov, L. N.; Shores, M. P.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7173–7175.
DOI:
10.1039/C4CC02297A
Synthesis and solid-state structures of a macrocyclic receptor based on the 2,6-bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine scaffold
J. M. Engle, P. S. Singh, C. L. Vonnegut, L. N. Zakharov, D. W. Johnson and M. M. Haley CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 3703-3706.
DOI:
10.1039/C3CE42307G
Selective Nitrate Binding in Competitive Hydrogen Bonding Solvents: Do Anion–π Interactions Facilitate Nitrate Selectivity?
Watt, M. M.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10275–10280.
DOI:
10.1002/anie.201303881
An Anion-Modulated Three-Way Supramolecular Switch that Selectively Binds Dihydrogen Phosphate, H2PO4−
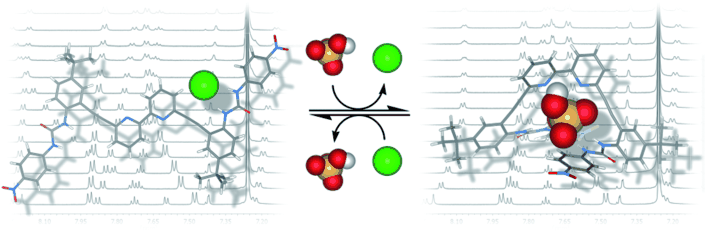
Gavette, J. V.; Mills, N. S.; Zakharov, L. N.; Johnson, C. A.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2013, 52, 10460–10464.
DOI:
10.1002/anie.201302929
Aryl C–H•••Cl− hydrogen bonding in a fluorescent anion sensor
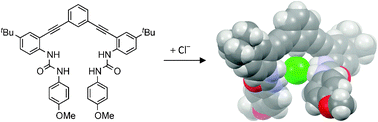
Tresca, B. W.; Zakharov, L. N.; Carroll, C. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7240-7242.
DOI:
10.1039/C3CC44574G
Lithium-selective phosphine oxide-based ditopic receptors show enhanced halide binding upon alkali metal ion coordination
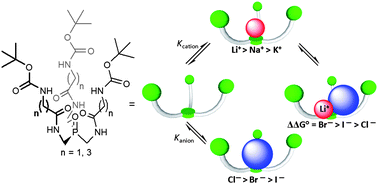
Gavette, J. V.; Lara, J.; Reling, L. L.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 585-590.
DOI:
10.1039/C2SC21501B
Synthesis and optoelectronic properties of 2,6-bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine scaffolds
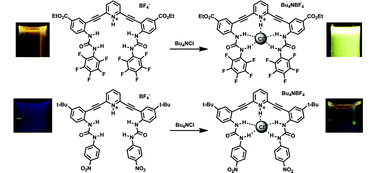
Engle, J. M.; Carroll, C. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1105-1110.
DOI:
10.1039/C2SC00975G
Molecular Self-Assembly: Solvent Guests Tune the Conformation of a series of 2,6-Bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine-Based Ureas
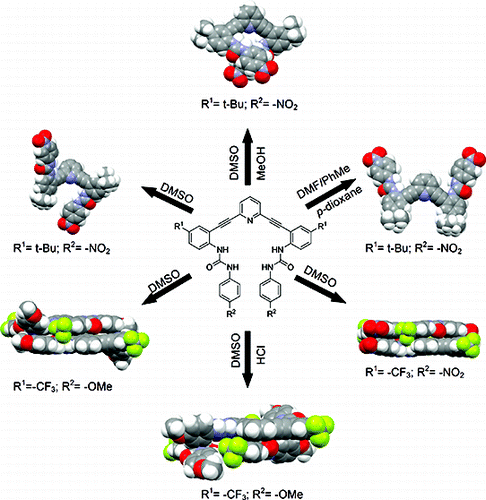
Engle, J. M.; Lakshminarayanan, P. S.; Carroll, C. N.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 5144-5152.
DOI:
10.1021/cg201074v
Lithium cation enhances anion binding in a tripodal phosphine oxide-based ditopic receptor
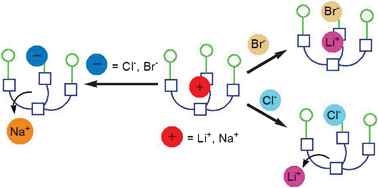
Gavette, J. V.; Lara, J.; Berryman, O. B.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7653-7655.
DOI:
10.1039/C1CC12475G
Anion-dependent fluorescence in bis(anilinoethynyl)pyridine derivatives: switchable ON–OFF and OFF–ON responses
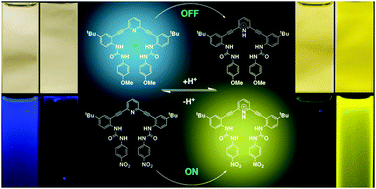
Carroll, C. N.; Coombs, B. A.; McClintock, S. P.; Johnson II, C. A.; Berryman, O. B.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5539-5541.
DOI:
10.1039/C1CC10947B
Arylethynyl receptors for neutral molecules and anions: emerging applications in cellular imaging
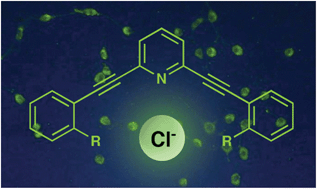
Carroll, C. N.; Naleway, J. J.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3875–3888.
DOI:
10.1039/B926231H
Anion Binding Induces Helicity in a Hydrogen-Bonding Receptor: Crystal Structure of a 2,6-Bis(anilinoethynyl)pyridinium Chloride
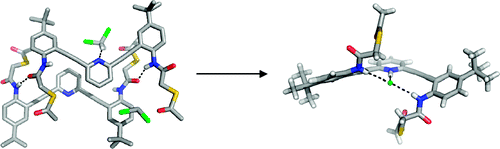
Johnson, C. A.; Berryman, O. B.; Sather, A. C.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson , D. W. Cryst. Growth Des., 2009, 9 (10), 4247–4249.
DOI:
10.1021/cg900674p
Protonation activates anion binding and alters binding selectivity in new inherently fluorescent 2,6-bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine bisureas
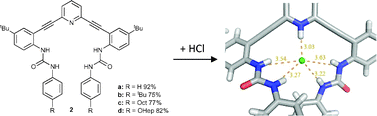
Carroll, C. N.; Berryman, O. B.; Johnson, C. A.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson, D. W. Chem. Commun. 2009, 18, 2520–2522.
DOI:
10.1039/B901643K
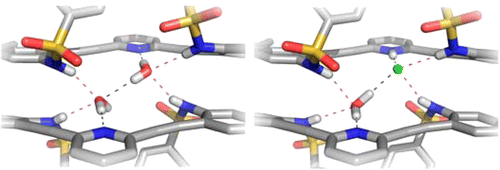
Water and Hydrogen Halides Serve the Same Structural Role in a Series of 2+2 Hydrogen-Bonded Dimers Based on 2,6-Bis(2-anilinoethynyl)pyridine Sulfonamide Receptors
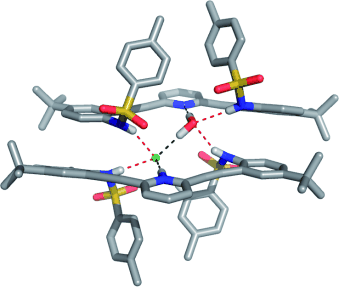
Berryman, O. B.; Johnson, C. A.; Zakharov, L. N.; Haley, M. M.; Johnson D. W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 117-120.
DOI:
10.1002/anie.200703971
